Difference between revisions of "PQplot"
(→Typical applications include) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
PQplot calculates inflow performance relationship (IPR) and vertical lift performance (VLP) curves for oil and gas wells. | PQplot calculates inflow performance relationship (IPR) and vertical lift performance (VLP) curves for oil and gas wells. | ||
| − | == Typical | + | == Typical application == |
* Estimation of flow rates | * Estimation of flow rates | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* Selection of wellhead pressures and surface choke sizing | * Selection of wellhead pressures and surface choke sizing | ||
* Estimation of the effects of reservoir pressure depletion | * Estimation of the effects of reservoir pressure depletion | ||
| − | * Identification of flow restrictions | + | * Identification of flow restrictions |
| − | |||
== Main features == | == Main features == | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 30 June 2017
Brief
PQplot calculates inflow performance relationship (IPR) and vertical lift performance (VLP) curves for oil and gas wells.
Typical application
- Estimation of flow rates
- Selection of tubing size
- Selection of flowline size
- Selection of wellhead pressures and surface choke sizing
- Estimation of the effects of reservoir pressure depletion
- Identification of flow restrictions
Main features
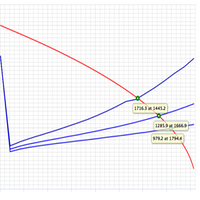
- Plot of Inflow performance curve (IPR) and Vertical lift performance curve (VLP)
- Rate and pressure at intersection point
- Sensitivity analysis of IPR and VLP curves on parameters
- Using prepared PVT models
- Inclined wells calculations
- Tubing, annular and both flow types
Interface features
- Save and share references to saved models with colleagues
- Last saved model on current computer and browser is automatically opened
- Choose between Metric units and US oilfield units
- Save as image and print plot by means of chart context menu (button at the upper-right corner of chart)
- Download report in pdf format containing input parameters, calculated values and plot
- Select and copy results to Excel or other application
Used correlations
| Type of problem | Correlation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Oil well VLP |
Hagedorn, A. R., & Brown, K. E. (1965). Experimental study of pressure gradients occurring during continuous two-phase flow in small-diameter vertical conduits. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 17(04), 475-484. | |
|
Gas well VLP |
Gray, H. E. (1974). Vertical flow correlation in gas wells. User manual for API14B, subsurface controlled safety valve sizing computer program. | |
|
Dry gas VLP |
Cullender, M.H. and Smith, R.V. 1956. Practical Solution of Gas-Flow Equations for Wells and Pipelines with Large Temperature Gradients. Trans., AIME 207: 281. | |
|
Oil well inflow |
Composite IPR based – Vogel equations taking into account water |
Kermit E. Brown "The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods" Vol. 4 Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis, p. 30, section 2.227.1 |
|
Gas well inflow – backpressure equation |
Rawlins and Schellhardt |
Rawlins, E.L. and Schellhardt, M.A. 1935. Backpressure Data on Natural Gas Wells and Their Application to Production Practices, Vol. 7. Monograph Series, USBM. |
|
Gas well inflow – pseudo-pressure equation using Jd and kh values |
Real-gas pseudopressure equation |
See for example: Ahmed, T., & McKinney, P. (2011). Advanced reservoir engineering. Gulf Professional Publishing. |
|
Turner |
Turner, R. G., Hubbard, M. G., and Dukler, A. E. (1969) “Analysis and Prediction of Minimum Flow Rate for the Continuous Removal of Liquids from Gas Wells,” Journal of Petroleum Technology, Nov. 1969. pp. 1475–1482. | |
|
Guidelines from API RP14E |
Mokhatab S, Poe WA, Speight JG (2006) "Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing", Section 11.6 - Design Considerations on sales gas pipelines, subsection 11.6.1 - Line Sizing Criteria, Elsevier, 2006. |
PVT correlations are the same as in PVT tool.