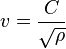Erosional velocity
From wiki.pengtools.com
By Mikhail Tuzovskiy on 20230103052848
Erosional velocity
Erosional velocity is a velocity of the multiphase flow at which pipe erosion occurs.
Erosional velocity equation
Pipe erosion begins when velocity exceeds the value of
where:
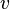 = gas velocity, ft/s
= gas velocity, ft/s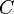 = empirical constant (starting erosional velocity), lb/s/ft2
= empirical constant (starting erosional velocity), lb/s/ft2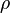 = gas density, lb/ft3
= gas density, lb/ft3
API RP 14E (1984) suggested C=100 for continuous and 125 for non continuous service.
Erosion
Erosion is a loss of original material due to solid particle impact on the material surface.
Erosion is normally expressed as a rate of metal loss, usually mm/year. It usually occurs in turns or protrusions; or with solids content.
One can relate Erosional velocity to a metal loss rate (see RP O501).
References
- Mokhatab S, Poe WA, Speight JG (2006) "Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing", Section 11.6 - Design Considerations on sales gas pipelines, subsection 11.6.1 - Line Sizing Criteria, Elsevier, 2006.