Well Nodal Analysis
Contents
Well Nodal Analysis
Well Nodal Analysis is the fundamental petroleum engineering technique published in 1979 by Joe Mach [1]. For his invention Joe Mach was honored as JPT Legend of Production and Operations in 2009[2].
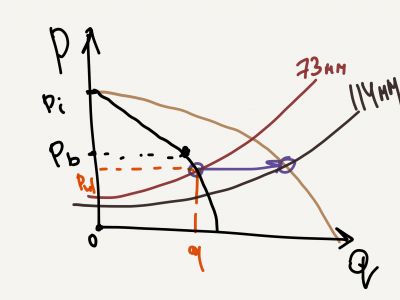
Well Nodal Analysis is used to predict the well rate and performance by combining the reservoir inflow with the wellbore lift capacity by intersecting the IPR and VLP curves on a pressure vs rate plot.
For the given reservoir Well Nodal Analysis calculates how much oil, water and gas can be produced by the given well.
New Petroleum Engineering Workflow
- Assess the current gas for oilfield performance. What is the current oil and gas production? Get organized with the available oil and gas production data.
- Calculate the Production Potential and identify the performance gaps in a form of Enhancement List.
- Close the performance gaps by executing identified Enhancements.
- Track the benefits achieved with the Enhancement Tracking.
Such a workflow can be applied both on a well level and on a oilfield pattern level. The petroleum engineer task is to keep wells at potential and patterns balanced while management should be held accountable that the prescribed actions are implemented in a timely manner[3].
Routine execution of described Petroleum Engineering Workflow results in more production, improved recovery and increased earnings.
Petroleum Engineering Technology
- Darcy's law
- Nodal Analysis
- Artificial Lift, especially Electrical Submersible Pumps
- Hydraulic fracturing
- Waterflooding
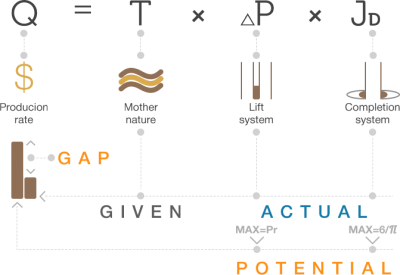
Petroleum Engineering Technology allows achieving Production Potential, which is maximum drawdown in the Lift System and maximum well's productivity index in the Completion System.
Oil and Gas production optimization challenges
The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. Reasons for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is well potentials are not known and therefore not managed. Introducing petroleum engineering workflow of maximizing oil and gas production in such oil and gas companies will usually face a resistance in a form of excuses why not to increase production. Below are top 10.
See also
References
- ↑
Mach, Joe; Proano, Eduardo; Brown, Kermit E. (1979). "A Nodal Approach For Applying Systems Analysis To The Flowing And Artificial Lift Oil Or Gas Well"
 (SPE-8025-MS). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
(SPE-8025-MS). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
- ↑
JPT, staff (2009). "Legends of Production and Operation"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-1209-0033-JPT).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-1209-0033-JPT).
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedDW