Difference between revisions of "Well Nodal Analysis"
(→Typical Applications) |
(→Well Nodal Analysis Workflow) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
Well [[VLP]] curve: [[Hagedorn and Brown]] multiphase flow correlation | Well [[VLP]] curve: [[Hagedorn and Brown]] multiphase flow correlation | ||
| − | ==Well Nodal Analysis | + | ==Well Nodal Analysis Example== |
The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. Reasons for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is well potentials are not known and therefore not managed. Introducing petroleum engineering workflow of maximizing oil and gas production in such oil and gas companies will usually face a resistance in a form of excuses why not to increase production. Below are top 10. | The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. Reasons for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is well potentials are not known and therefore not managed. Introducing petroleum engineering workflow of maximizing oil and gas production in such oil and gas companies will usually face a resistance in a form of excuses why not to increase production. Below are top 10. | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 30 May 2020
Contents
Well Nodal Analysis
Well Nodal Analysis is the fundamental petroleum engineering technique published in 1979 by Joe Mach [1]. For his invention Joe Mach was honored as a JPT Legend of Production and Operations in 2009[2].
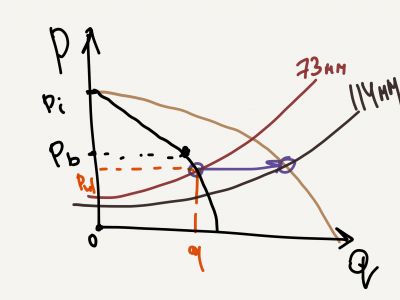
Well Nodal Analysis is used to predict the well rate and performance by combining the reservoir inflow with the wellbore lift capacity by intersecting the IPR and VLP curves on a pressure vs rate plot.
For the given reservoir Well Nodal Analysis calculates how much oil, water and gas can be produced by the given well.
Well Nodal Analysis software is available online at www.pengtools.com.
The Power of Well Nodal Analysis
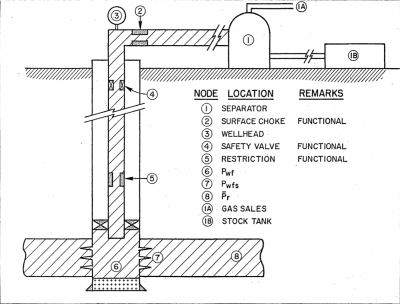
Well Nodal Analysis is the cornerstone of petroleum engineering. It allows to:
- Calculate the well production potential and identify the performance gaps to maximize oil and gas production.
- Evaluate the various well nodes impact on production. Nodes: reservoir, perforation, tubing string, restrictions, downhole safety valves, the surface chokes, the surface flow lines and separator.
Typical Applications
- Estimation of well production potential and absolute open flow (AOF)
- Tubing sizing
- Selection of the operating wellhead pressures
- Artificial lift design. Gas lift. ESP sizing.
- Sensitivity studies
Math and Physics
Well Nodal Analysis is done on a pressure vs rate plot. IPR and VLP curves intersect at well operating point.
Well IPR curve: Darcy's law, Vogel's IPR, Composite IPR.
Well VLP curve: Hagedorn and Brown multiphase flow correlation
Well Nodal Analysis Example
The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. Reasons for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is well potentials are not known and therefore not managed. Introducing petroleum engineering workflow of maximizing oil and gas production in such oil and gas companies will usually face a resistance in a form of excuses why not to increase production. Below are top 10.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1
Mach, Joe; Proano, Eduardo; Brown, Kermit E. (1979). "A Nodal Approach For Applying Systems Analysis To The Flowing And Artificial Lift Oil Or Gas Well"
 (SPE-8025-MS). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
(SPE-8025-MS). Society of Petroleum Engineers.
- ↑
JPT, staff (2009). "Legends of Production and Operation"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-1209-0033-JPT).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-1209-0033-JPT).