Difference between revisions of "Category: Mature Water Flood Analysis"
(→Workflow) |
(→Workflow) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
#Upload the required data | #Upload the required data | ||
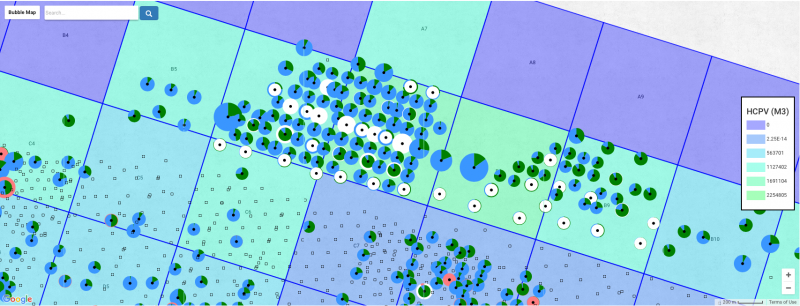
#Gridding - Divide the field into [[Pattern]]s/[[Block]]s/[[Bucket]]s using the [[Bubble map]] by identifying dominant no-flow boundaries. '''No-flow boundary''' is a line in the reservoir where reservoir fluids do not cross. Oil and water on either side of the line flow away from this line. | #Gridding - Divide the field into [[Pattern]]s/[[Block]]s/[[Bucket]]s using the [[Bubble map]] by identifying dominant no-flow boundaries. '''No-flow boundary''' is a line in the reservoir where reservoir fluids do not cross. Oil and water on either side of the line flow away from this line. | ||
| + | #Calculate well allocation factors WAF for blocks\patterns | ||
#Calculate [[HCPV]], [[HCPVinj]], RF, VRR, VRRcum for each reservoir using blocks | #Calculate [[HCPV]], [[HCPVinj]], RF, VRR, VRRcum for each reservoir using blocks | ||
#Match total [[HCPV]] to [[STOIIP]] numbers by changing the edge [[Block]]s areas | #Match total [[HCPV]] to [[STOIIP]] numbers by changing the edge [[Block]]s areas | ||
Revision as of 11:01, 23 March 2022
Contents
Brief
Mature Water Flood Analysis is a workflow for identifying the performance gaps in the mature waterfloods performance.
Mature Water Flood Analysis is applied to the Reservoirs and uses Monthly Measures for production/injection data.
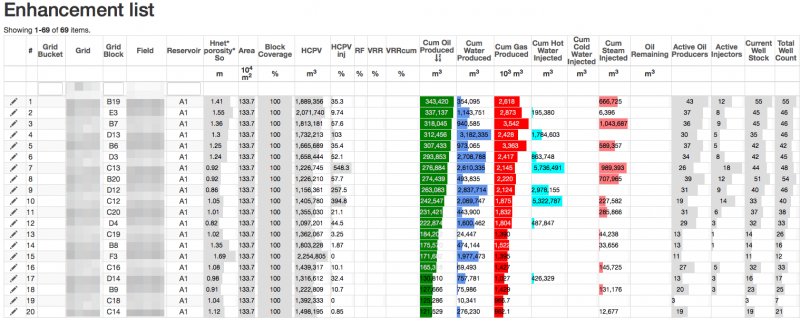
As a result Mature Water Flood Analysis generates Blocks/Patterns Enhancement List.
The goal of the waterflooding
The goal of the water flooding is to inject the least possible water to produce the most possible oil in the shortest possible time.
Workflow
- Upload the required data
- Gridding - Divide the field into Patterns/Blocks/Buckets using the Bubble map by identifying dominant no-flow boundaries. No-flow boundary is a line in the reservoir where reservoir fluids do not cross. Oil and water on either side of the line flow away from this line.
- Calculate well allocation factors WAF for blocks\patterns
- Calculate HCPV, HCPVinj, RF, VRR, VRRcum for each reservoir using blocks
- Match total HCPV to STOIIP numbers by changing the edge Blocks areas
- Make Plots (by field, by reservoir, by block): History, RF vs HCPVinj, RF vs well spacing, WOR vs Np, VRR vs t
- Make Maps (by reservoir) showing Blocks: HCPV, HCPVinj, RF, VRR
- Make Cross sections
- Calculate Blocks Enhancement List
- Create Action List
- Execute
Repeat steps 5-6-7-8-9-10 routinely (monthly, quarterly, half year).
Data Required
- Create Fields
- Upload Reservoirs
- Upload PVT
- Upload Wells
- Upload Deviation Surveys
- Upload Perforations
- Upload Well Log Interpretations
- Upload Monthly Measures
Action List
The typical actions are:
- Convert producing well to injector
- Shut in inefficient injection well, water-cyclers
- Increase/Decrease well injection rate
- Add/squeeze Perforations at producing or injection wells
- Drill infill production/injection well
References
Wolcott, D. ; Applied Waterflood Field Development, Energy Tribune Publishing Inc., 2009.
Pages in category "Mature Water Flood Analysis"
The following 12 pages are in this category, out of 12 total.