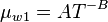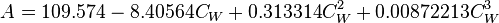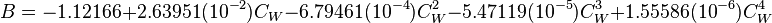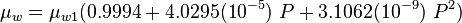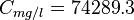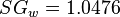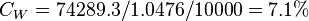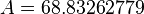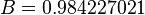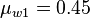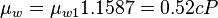Difference between revisions of "Water viscosity"
From wiki.pengtools.com
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| + | :[[Water bubble point pressure]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water compressibility]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water density]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water formation volume factor]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water salinity from density equation]]<BR/> | ||
:[[Water solids concentration]]<BR/> | :[[Water solids concentration]]<BR/> | ||
| − | + | :[[Water viscosity]]<BR/> | |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
Revision as of 06:23, 5 October 2020
Contents
Water viscosity
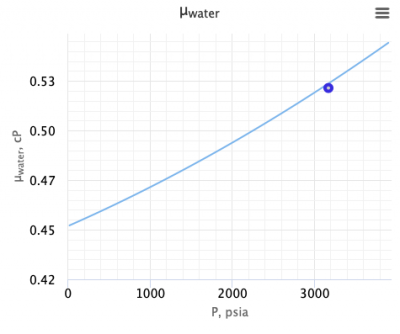
Water viscosity correlation is published by McCain in 1991[1].
Math and Physics
where
Example. Calculating water viscosity
Input data
Calculate water viscosity at 3176 psia and 165°F?
Solution
Nomenclature
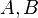 = coefficients
= coefficients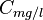 = pressure correction, res bbl/STB
= pressure correction, res bbl/STB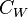 = water salinity or weight percent solids, %
= water salinity or weight percent solids, % = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia = Temperature, °F
= Temperature, °F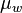 = water viscosity, cP
= water viscosity, cP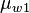 = water viscosity at 1 atm, cP
= water viscosity at 1 atm, cP
See also
- Water bubble point pressure
- Water compressibility
- Water density
- Water formation volume factor
- Water salinity from density equation
- Water solids concentration
- Water viscosity