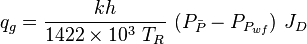Difference between revisions of "Vogel's IPR"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math and Physics) |
(→Math and Physics) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*[[Darcy's law]] inflow equation for the single phase incompressible liquid: | *[[Darcy's law]] inflow equation for the single phase incompressible liquid: | ||
| − | :<math> \frac{q_o}{ | + | :<math> \frac{q_o}{q_o_{max}} = 1-0.2 \frac{P_{wf}}{\bar{P}} - 0.8 \left ( \frac{P_{wf}}{\bar{P}} \right )^2</math> |
*[[Vogel's IPR]] two phase equation (oil + gas) and it's combination with single phase liquid | *[[Vogel's IPR]] two phase equation (oil + gas) and it's combination with single phase liquid | ||
Revision as of 08:21, 5 April 2019
Contents
Vogel's Inflow Performance Relationship
Vogel's IPR[1]
Vogel's IPR is an empirical two-phase (oil + gas) inflow performance relationship correlation published in 1968 [1].
Vogel's IPR is based on computer simulations to several solution gas drive reservoirs for different fluid and reservoir relative permeability properties.
Vogel's IPR is the default IPR correlation for the oil wells in the PQplot.
Why Vogel's IPR?
Vogel's IPR solution has been found to be very good and is widely used in prediction of IPR curves.— Kermit Brown et al[2]
Math and Physics
Oil well IPR equation
- Darcy's law inflow equation for the single phase incompressible liquid:
- Failed to parse (PNG conversion failed; check for correct installation of latex and dvipng (or dvips + gs + convert)): \frac{q_o}{q_o_{max}} = 1-0.2 \frac{P_{wf}}{\bar{P}} - 0.8 \left ( \frac{P_{wf}}{\bar{P}} \right )^2
- Vogel's IPR two phase equation (oil + gas) and it's combination with single phase liquid
- Composite IPR three phase equation (oil + gas + water)
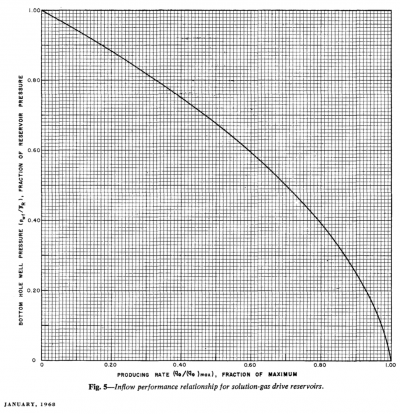
Gas well IPR equation
- Darcy's law gas inflow equation:
- C and n equation
IPR calculator software
- PQplot nodal analysis software is used to calculate the IPR curves. PQplot is available online at www.pengtools.com.
- Excel
- other
Nomenclature
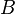 = formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= formation volume factor, bbl/stb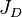 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless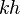 = permeability times thickness, md*ft
= permeability times thickness, md*ft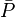 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia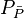 = average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP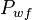 = well flowing pressure, psia
= well flowing pressure, psia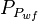 = average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP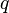 = flowing rate, stb/d
= flowing rate, stb/d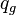 = gas rate, MMscfd
= gas rate, MMscfd = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R
Greek symbols
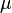 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Vogel, J. V. (1968). "Inflow Performance Relationships for Solution-Gas Drive Wells". Journal of Petroleum Technology. 20 (SPE-1476-PA).
- ↑ Brown, Kermit (1984). The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods. Volume 4. Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis. Tulsa, Oklahoma: PennWellBookss.