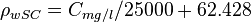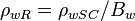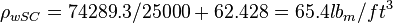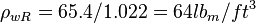Difference between revisions of "Water density"
From wiki.pengtools.com
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | == | + | ==Formation water density== |
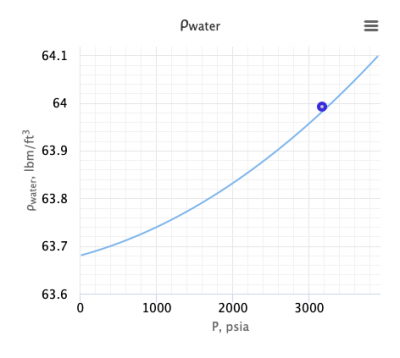
| − | [[File:Water density.png|thumb|right| | + | [[File:Water density.png|thumb|right|400px|Water density correlation in the PVT software at pengtools.com]] |
| − | The density of formation water (brine) at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F) | + | The density of formation water (brine) at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F): |
| − | :<math> \rho_{wSC} = C_{mg/l}/25000 + 62.428</math> | + | :<math> \rho_{wSC} = C_{mg/l}/25000 + 62.428</math><ref name= M1990/> |
| − | The density of formation water (brine) at reservoir conditions | + | The density of formation water (brine) at reservoir conditions: |
| − | :<math> \rho_{wR}= | + | :<math> \rho_{wR}=\rho_{wSC}/B_w </math><ref name= M1990/> |
==Example. Calculating formation water density == | ==Example. Calculating formation water density == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Input data=== | ===Input data=== | ||
:<math> C_{mg/l} = 74289.3 </math> | :<math> C_{mg/l} = 74289.3 </math> | ||
| + | :<math> B_w = 1.022 </math> at 3176 psia and 165°F | ||
Estimate the density of the brine at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F) and at 3176 psia and 165°F? | Estimate the density of the brine at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F) and at 3176 psia and 165°F? | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
:<math> \rho_{wSC} = 74289.3/25000 + 62.428 = 65.4 lb_m/ft^3</math> | :<math> \rho_{wSC} = 74289.3/25000 + 62.428 = 65.4 lb_m/ft^3</math> | ||
| + | :<math> \rho_{wR} = 65.4/1.022= 64 lb_m/ft^3</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The solution is also available in the PVT software model at [The solution is available in the PVT calculator software model at [https://www.pengtools.com/pvtCalculator?paramsToken=d0f0c9c587152cefc27d1217e091ace0 www.pengtools.com] | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 31: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| + | :[[Water bubble point pressure]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water compressibility]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water density]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water formation volume factor]]<BR/> | ||
| + | :[[Water salinity from density equation]]<BR/> | ||
:[[Water solids concentration]]<BR/> | :[[Water solids concentration]]<BR/> | ||
| − | + | :[[Water viscosity]]<BR/> | |
| + | :[[Gas/Water Interfacial Tension]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| Line 41: | Line 51: | ||
|ISBN=978-0878143351 | |ISBN=978-0878143351 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:16, 5 October 2020
Contents
Formation water density
The density of formation water (brine) at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F):
The density of formation water (brine) at reservoir conditions:
Example. Calculating formation water density
Example source [1]
Input data
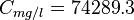
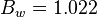 at 3176 psia and 165°F
at 3176 psia and 165°F
Estimate the density of the brine at standard conditions (14.7psia & 60°F) and at 3176 psia and 165°F?
Solution
The solution is also available in the PVT software model at [The solution is available in the PVT calculator software model at www.pengtools.com
Nomenclature
 = water formation volume factor, res bbl/STB
= water formation volume factor, res bbl/STB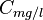 = water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l
= water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l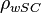 = water density at standard conditions, lbm/ft3
= water density at standard conditions, lbm/ft3
See also
- Water bubble point pressure
- Water compressibility
- Water density
- Water formation volume factor
- Water salinity from density equation
- Water solids concentration
- Water viscosity
- Gas/Water Interfacial Tension
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351.