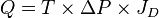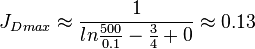Difference between revisions of "Production Potential"
(→Maximum J_D) |
(→Maximum J_D) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Maximum <math>J_D</math>== | ==Maximum <math>J_D</math>== | ||
| + | The unstimulated vertical well potential in a pseudo steady radial flow is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> {J_D}_{max} \approx \frac{1}{ln{\frac{500}{0.1}-\frac{3}{4}+0}} \approx 0.13</math> | ||
The maximum possible stimulated well potential for pseudo steady linear flow is: | The maximum possible stimulated well potential for pseudo steady linear flow is: | ||
| − | <math>{J_D}_{max}= \frac{6}{\pi} \approx 1.91 </math> | + | <math>{J_D}_{max}= \frac{6}{\pi} \approx 1.91 </math> , see [[6/π stimulated well potential]] |
The maximum possible stimulated well potential for steady state linear flow is: | The maximum possible stimulated well potential for steady state linear flow is: | ||
| Line 46: | Line 49: | ||
Can [[Production Potential]] be achieved? | Can [[Production Potential]] be achieved? | ||
| − | The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. [[29+ reasons why you can not increase the production |Reasons]] for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is [[Production Potential]] is not known and therefore not managed. | + | The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. [[29+ reasons why you can not increase the production |Reasons]] for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is [[Production Potential]] is not known and therefore not managed<ref name=DW />. |
Calculating the [[Production Potential]] opens the pathway to achieve potential. | Calculating the [[Production Potential]] opens the pathway to achieve potential. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | [[JD]]<BR/> | ||
| + | [[6/π stimulated well potential]]<BR/> | ||
| + | [[4/π stimulated well potential]]<BR/> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 69: | Line 77: | ||
[[Category:Enhancement List]] | [[Category:Enhancement List]] | ||
[[Category:E&P Portal]] | [[Category:E&P Portal]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{#seo: | ||
| + | |title=Production Potential | ||
| + | |titlemode= replace | ||
| + | |keywords=production potential, oil and gas production, oil production, oil and gas production optimization | ||
| + | |description=Production Potential is the maximum rate that can be delivered through oil and gas production optimization | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:45, 8 July 2023
Contents
Brief
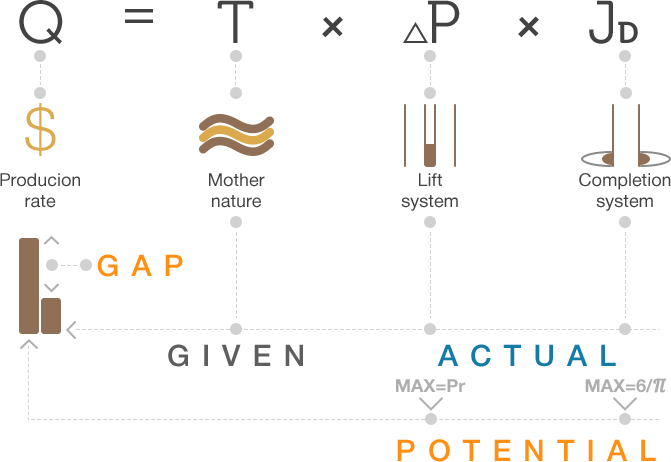
Production Potential is the maximum rate that can be delivered by Well, Pattern, Block or Reservoir.
Math and Physics
The Darcy's law can be written as:
where:
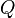 is the oil or gas production rate,
is the oil or gas production rate, is the Reservoir transmissibility and is given by the Mother Nature,
is the Reservoir transmissibility and is given by the Mother Nature,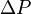 is the Lift System Drawdawn which is set by the operational engineering practices[1],
is the Lift System Drawdawn which is set by the operational engineering practices[1],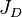 is the Completion System dimensionless productivity index which is set by the design engineering practices[1].
is the Completion System dimensionless productivity index which is set by the design engineering practices[1].
The rate 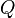 is maximum then
is maximum then 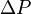 and
and 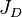 are maximum.
are maximum.
Maximum 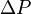
The drawdown is:
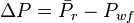
The maximum drawdown is reached then the flowing bottomhole pressure, 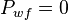 , so:
, so:
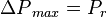
Maximum 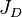
The unstimulated vertical well potential in a pseudo steady radial flow is:
The maximum possible stimulated well potential for pseudo steady linear flow is:
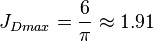 , see 6/π stimulated well potential
, see 6/π stimulated well potential
The maximum possible stimulated well potential for steady state linear flow is:
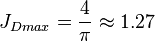 , see 4/π stimulated well potential
, see 4/π stimulated well potential
Achieving potential
Can Production Potential be achieved?
The ideal, of producing and recovering at potential, is rarely obtained in practice. Reasons for this vary from company to company, but more often than not, the reason is Production Potential is not known and therefore not managed[1].
Calculating the Production Potential opens the pathway to achieve potential.
See also
JD
6/π stimulated well potential
4/π stimulated well potential
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.