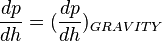Difference between revisions of "VLP"
(→Math and Physics) |
(→Math and Physics) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
To do it we need to solve the Energy balance equation. | To do it we need to solve the Energy balance equation. | ||
| − | :<math>frac{dp}{dh}=(frac{dp}{dh})_{GRAVITY}</math> | + | :<math>\frac{dp}{dh}=(\frac{dp}{dh})_{GRAVITY}</math> |
This equation relates the pressure to the distance for the given mass. | This equation relates the pressure to the distance for the given mass. | ||
Revision as of 06:44, 27 April 2020
Vertical Lift Performance
Vertical Lift Performance curve is a relationship between the flow rate and the pressure.
VLP curve shows how much pressure required to lift a certain amount of fluid to the surface at the given well head pressure.
VLP curve is used in Nodal Analysis for production systems design, analysis and optimization.
Math and Physics
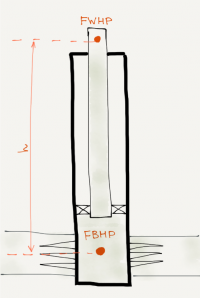
This is a wellbore schematic. We have the reservoir, perforations, bottomhole, completion string and the wellhead.
The depth of the well is h. The two pressure points of importance are flowing bottom hole pressure FBHP and flowing well head pressure FWHP.
To build the VLP curve we need to calculate the bottom hole pressure given the well head pressure and the well rate.
To do it we need to solve the Energy balance equation.
This equation relates the pressure to the distance for the given mass.
It has 3 terms: Gravity, Friction and Kinetic.
To find the required lift pressure we need to integrate this equation over the fluid’s travel distance.
All available VLP correlations are solving the same equation.
The differences are usually in the way how the friction term is calculated.
Let’s look how the Hagedorn and Brown correlation handles this equation.
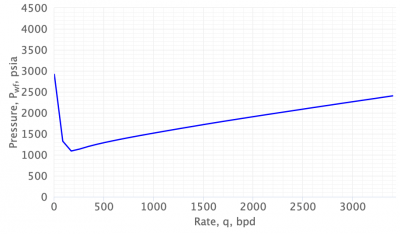
This VLP curve was calculated using the Hagedorn and Brown.
You can see what the higher the rate the higher the pressure required. This is related to the friction forces.
On the other hand the hook right here is caused by the liquid dominating gas.
VLP calculator software
- PQplot nodal analysis software is used to calculate the VLP curves. PQplot is available online at www.pengtools.com.
- Excel
- other