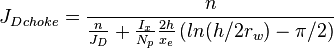Category: OptiFracMS
Contents
Multistage Fracturing Software
optiFracMS is a software to optimize the number of hydraulic fractures in horizontal well [1].
For the given set of reservoir properties and the proppant mass optiFracMS calculates optimal number of transverse hydraulic fractures and required fractures geometry to maximize well productivity index.
optiFracMS is available online at www.pengtools.com.
Typical applications
- Multistage Fracturing Design in tight oil and gas reservoirs
- How many fractures are required to maximize production?
- Number of fractures, n.
- What fractures geometry is required to maximize production?
- Dimensionless Fracture conductivity, CfD .
- Fracture half length, Xf .
- Fracture width, w .
- Fracture penetration, Ix .
- What would be the optimal productivity index?
- Dimensionless productivity index, JD .
- How many fractures are required to maximize production?
- Multistage Post fracture performance reviews
- Find out how far your well's productivity from where it should be (from the optimum)
- Multistage Fracturing Sensitivity Studies and Benchmarking
Math & Physics
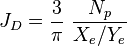 - technical potential for multistage fracturing [1],
- technical potential for multistage fracturing [1],
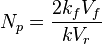 - proppant number,
- proppant number,
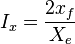 - penetration ratio,
- penetration ratio,
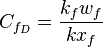 - dimensionless fracture conductivity,
- dimensionless fracture conductivity,
Type Curves
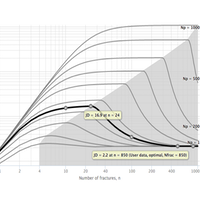
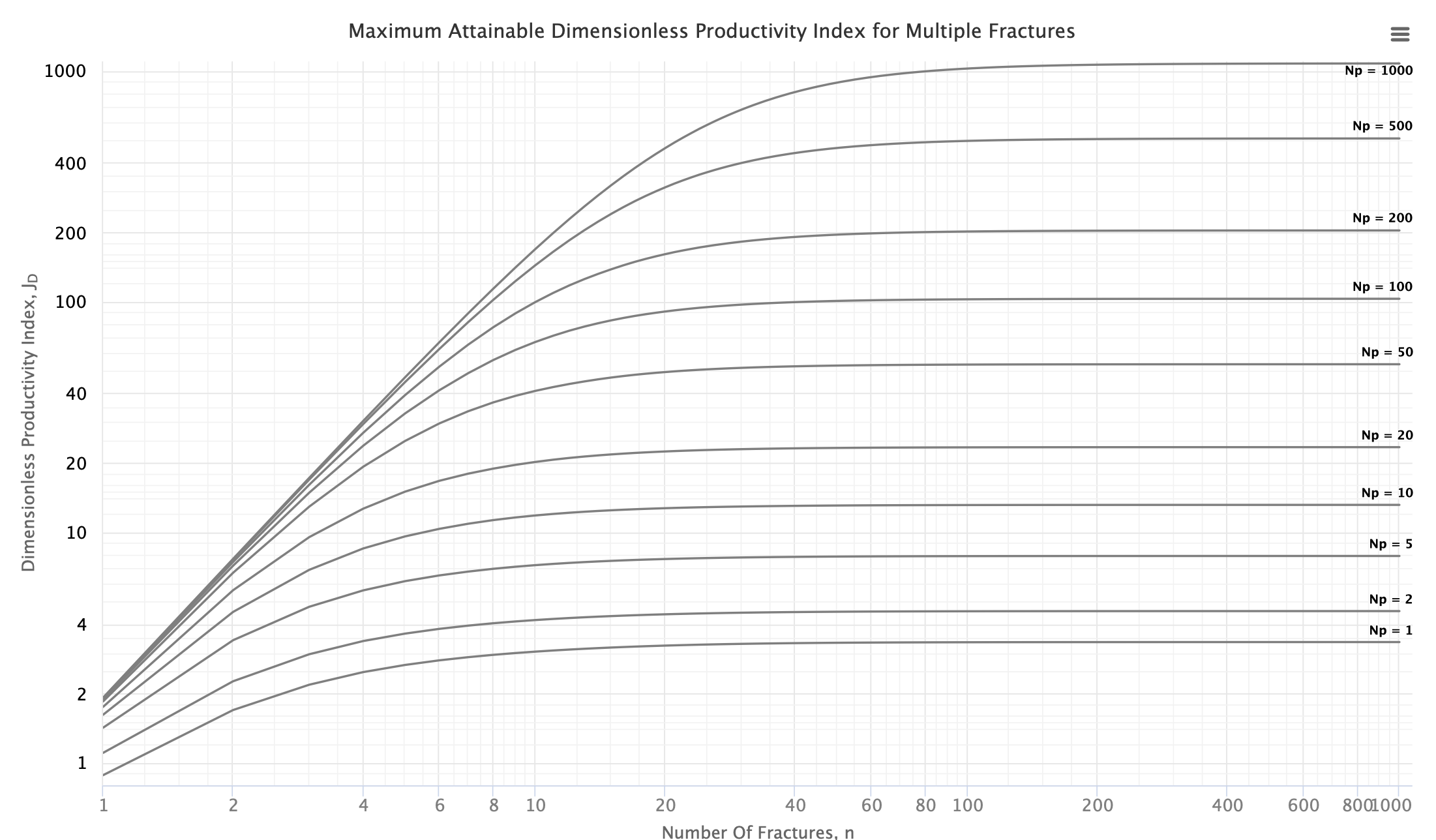
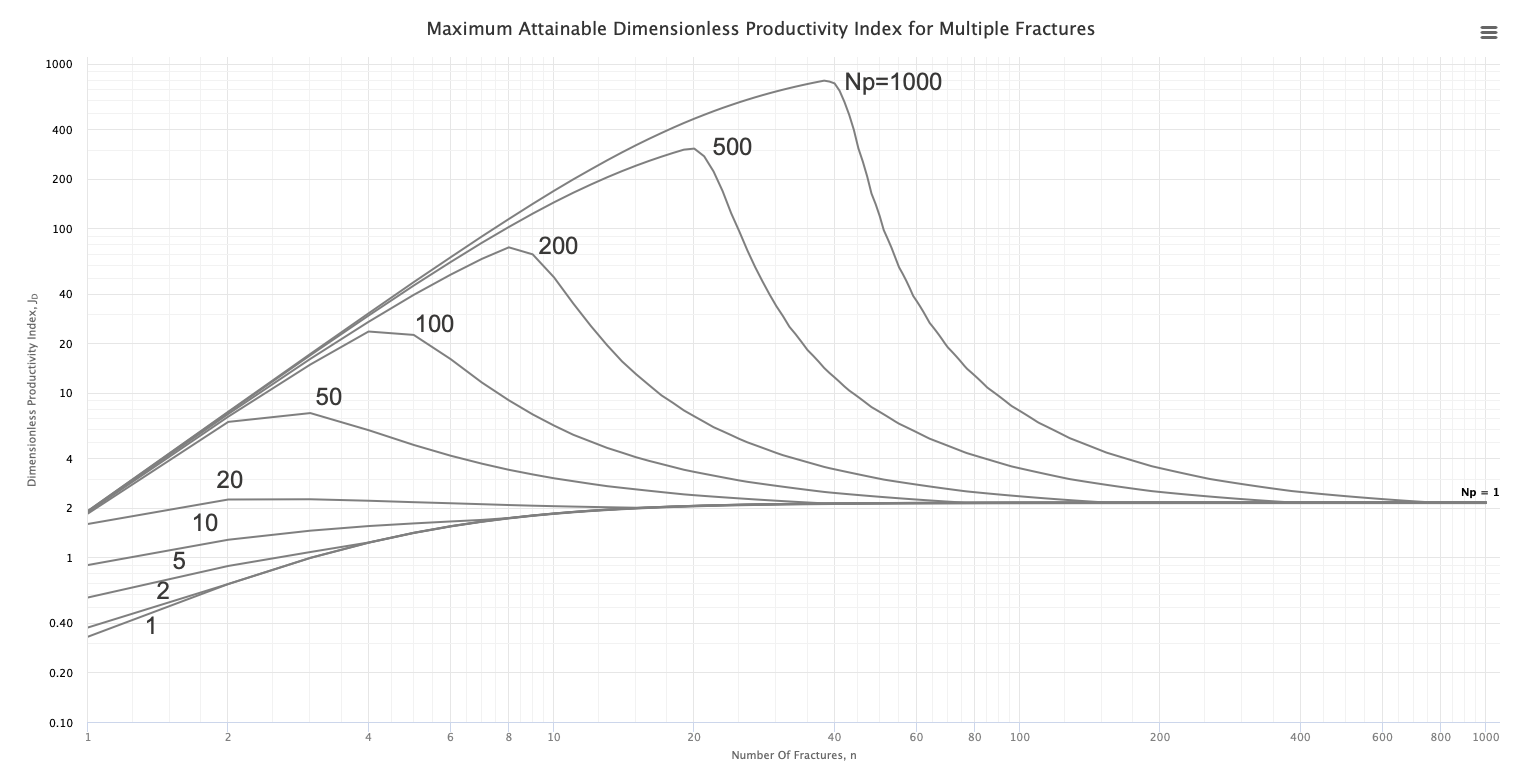
The type curves show multistage fracturing dimensionless productivity index, JD , at pseudo-steady state as a function of number of fractures, n and proppant number, Np for a horizontal well with multiple transverse hydraulic fractures in a square drainage area.
Type Curves were obtained, through 28,000 runs with direct boundary element (DBE) method [1].
For the given proppant number, Np, the more fractures that are created the higher the well JD. This is achieved by increasing the number of fractures, n, at the expense of individual fracture half-length and/or width. However, at some point, the additional increase in the number of fractures will result in fractures that are too slim to be practical. Such constrain is addressed below.
These type curves are also applicable for the case of rectangular (nonsquare) drainage areas.
Modification to rectangular (nonsquare) drainage areas
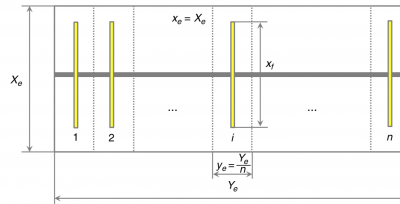
The modification needed for a rectangular well drainage is to divide both number of fractures and the corresponding JD by (Xe/Ye) [1].
Physical Constraints of the Multistage Fracturing
Choke skin
Choke skin is defined as the additional pressure loss because of convergence of flow in the vertical fracture to the horizontal wellbore.
Choke skin can be calculated as follows:
The effect of choke skin does not change the behavior of JD vs. n type curve, but but reduces maximum JD by as much as 9% [1].
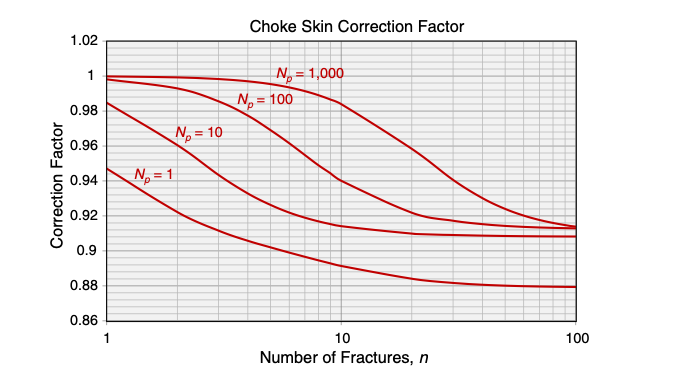
The correction factor as a function of n for xe/h = 65 and h/rw=250 [1].
The choke skin effect increases with the number of fractures, however this dependence finally flattens out.
Minimum fracture width constraint
To maintain fracture permeability kf, at least three proppant grains of width are required [2].
To account for this practical requirement, the deviation from the technical optimum will be required[2]. Instead of further decreasing the fracture width, the only possible option for a further increase in the number of fractures will be to decrease each fracture half-length. This will result in suboptimal performance of each fracture and, hence, suboptimal performance of the whole system in comparison to the ideal case without the minimum practical fracture width.
Effect of applying minimum fracture width constraint to the type curves (k=0.01md, kf=100d, xe=1609m, wmin=2.1mm) [1].
For the given proppant number, Np (above 20), there is an optimal number of fractures, n, with maximum well JD. Further increase in the number of fractures, n, will sharply decrease JD, because the fracture length is reduced to maintain the minimum width constraint for ever-reducing proppant volume per fracture.
Economic optimization of the Multistage Fracturing
The optimal number of stages seen above are strictly technical and do not include any cost and money value effects. Instead, these type curves can be used for the process of further economic optimization. Knowing the functional relationship between JD, NP, and n, and the cost of adding NP and n, the economic optimum can more readily be calculated [1].
Flow Diagram
Workflow
Case Study
Main features
- Plot of JD as a function of n and Np as parameter.
- Plot of JD as a function of Np showing the width constraint influence.
- Plot of JD and wf as a function of n for the given Np .
- Plot of JD as a function of CfD for the given n.
- Design optimization curves which corresponds to the maximum JD values for different Np and n.
- Optimum number of fractures n and well JD.
- Practical constrains envelope – minimum fracture width and choke skin effect.
- Sensitivity for the different from the optimal n, Xf, Ix, CfD, wf.
- Hydraulic fracturing proppant catalog with the predefined proppant properties.
Interface features
- Save and share models with colleagues
- Last saved model on current computer and browser is automatically opened
- Metric and US oilfield units
- Save as image and print plots by means of chart context menu (button at the upper-right corner of chart)
- Download pdf report with input parameters, calculated values and plots
- Select and copy results to Excel or other applications
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Guk, Vyacheslav; Tuzovskiy, Mikhail; Wolcott, Don; Mach, Joe (June 2019). "Optimizing Number of Fractures in Horizontal Well"
 . SPE Journal. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 24 (SPE-174772-PA).
. SPE Journal. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 24 (SPE-174772-PA).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Economides, Michael J.; Oligney, Ronald; Valko, Peter (2002). Unified Fracture Design: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice. Alvin, Texas: Orsa Press.
Pages in category "OptiFracMS"
The following 7 pages are in this category, out of 7 total.