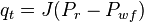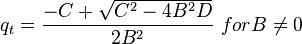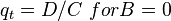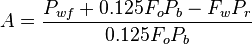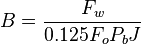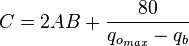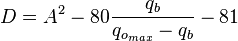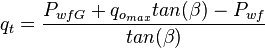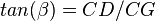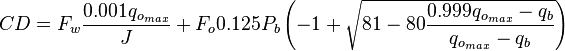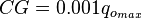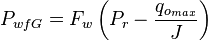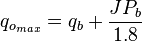Composite IPR
Contents
Composite Inflow Performance Relationship
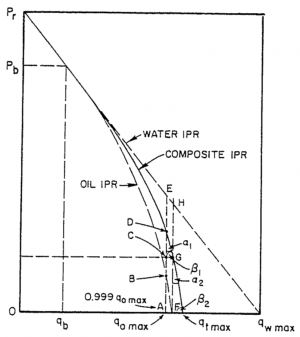
Composite IPR calculates IPR curve for oil wells producing water at various watercuts.
Composite IPR equation was derived by Petrobras based on combination of Vogel's IPR equation for oil flow and constant productivity for water flow [1].
Composite IPR curve is determined geometrically from those equations considering the fractional flow of oil and water [1].
Math and Physics
Total flow rate equations:
For Pb < Pwf < Pr
For pressures between reservoir pressure and bubble point pressure:
For PwfG < Pwf < Pb
For pressures between the bubble point pressure and the flowing bottom-hole pressures:
where:
For 0 < Pwf < PwfG
where:
And
Composite IPR calculation example
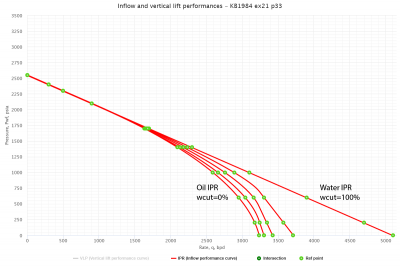
Following the example problem #21, page 33 [1]:
Given:
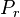 = 2550 psi
= 2550 psi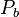 = 2100 psi
= 2100 psi
Test data:
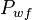 = 2300 psi
= 2300 psi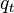 = 500 b/d
= 500 b/d
Calculate:
Determine the Composite IPR curves for Fw=0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.
Solution:
The problem was run through PQplot software for different values of watercut.
Result Composite IPR curves are shown on Fig.1. Points indicate results obtained by Brown [1].
The PQplot model from this example is available online by the following link: Composite IPR calculation example
Nomenclature
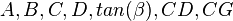 = calculation variables
= calculation variables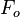 = oil fraction, fraction
= oil fraction, fraction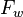 = water fraction, fraction
= water fraction, fraction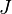 = productivity index, stb/d/psia
= productivity index, stb/d/psia = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia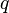 = flowing rate, stb/d
= flowing rate, stb/d
Subscripts
- b = at bubble point
- max = maximum
- o = oil
- r = reservoir
- t = total
- wf = well flowing bottomhole pressure
- wfG = well flowing bottomhole pressure at point G