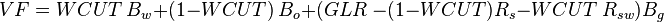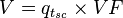Difference between revisions of "3 Phase IPR"
(→Math and Physics) |
(→Math and Physics) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
:<math> V=q_{t_{sc}} \times VF</math> <ref name=KermitBrown1984/> | :<math> V=q_{t_{sc}} \times VF</math> <ref name=KermitBrown1984/> | ||
| − | :<math> q_{t_{sc}} </math> | + | :<math> q_{t_{sc}} </math> is calculated as usual using: |
*[[Vogel's IPR]] | *[[Vogel's IPR]] | ||
*[[Composite IPR]] | *[[Composite IPR]] | ||
Revision as of 07:13, 17 April 2019
Contents
Three-phase Inflow Performance Relationship
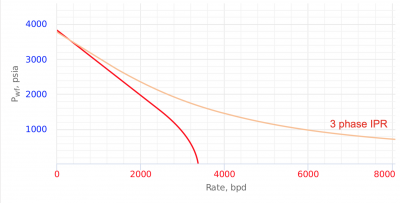
3 Phase IPR is an IPR curve calculated on the basis of total barrels of produced fluid, including gas.
3 Phase IPR curve is used in Pump Design software for pump sizing.
Math and Physics
The volume of 1 stb of liquid plus associated gas (volume factor) at any pressure and temperature is given by[1]:
The total volume of produced fluid rate (liquid plus gas) at any conditions of pressure and temperature:
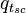 is calculated as usual using:
is calculated as usual using:
3 Phase IPR calculation example
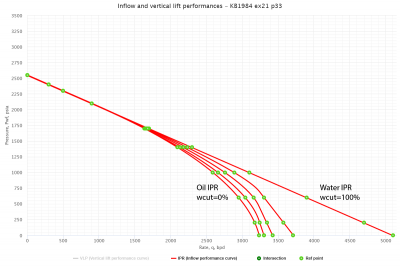
Following the example problem #21, page 33 [1]:
Given:
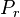 = 2550 psi
= 2550 psi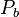 = 2100 psi
= 2100 psi
Test data:
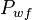 = 2300 psi
= 2300 psi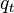 = 500 b/d
= 500 b/d
Calculate:
Determine the 3 Phase IPR curves for Fw=0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.
Solution:
The problem was run through PQplot software for different values of watercut.
Result 3 Phase IPR curves are shown on Fig.1. Points indicate results obtained by Brown [1].
The PQplot model from this example is available online by the following link: 3 Phase IPR calculation example
Nomenclature
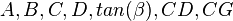 = calculation variables
= calculation variables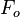 = oil fraction, fraction
= oil fraction, fraction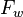 = water fraction, fraction
= water fraction, fraction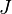 = productivity index, stb/d/psia
= productivity index, stb/d/psia = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia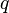 = flowing rate, stb/d
= flowing rate, stb/d
Subscripts
- b = at bubble point
- max = maximum
- o = oil
- r = reservoir
- t = total
- wf = well flowing bottomhole pressure
- wfG = well flowing bottomhole pressure at point G