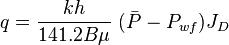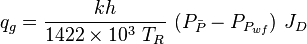Difference between revisions of "IPR"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Oil well IPR equation) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[File:Inflow Performance Relationship.png|thumb|right|400px|link=https://www.pengtools.com/pqPlot|Inflow Performance Relationship Curve]] | [[File:Inflow Performance Relationship.png|thumb|right|400px|link=https://www.pengtools.com/pqPlot|Inflow Performance Relationship Curve]] | ||
| − | [[IPR]] is a curve of producing rates plotted against well bottomhole pressures. | + | [[IPR]] is a curve of producing rates plotted against well bottomhole pressures <ref name= Vogel/>. |
[[IPR]] curve shows productive capacity and performance of a well. | [[IPR]] curve shows productive capacity and performance of a well. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:pengtools]] | [[Category:pengtools]] | ||
| + | === References === | ||
| + | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name=Vogel>{{cite journal | ||
| + | |last1= Vogel |first1=J. V. | ||
| + | |title=Inflow Performance Relationships for Solution-Gas Drive Wells | ||
| + | |journal=Journal of Petroleum Technology | ||
| + | |volume=20 | ||
| + | |issue=01 | ||
| + | |number=SPE-1476-PA | ||
| + | |date=1968 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </references> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
:[[141.2 derivation]]<BR/> | :[[141.2 derivation]]<BR/> | ||
Revision as of 06:49, 5 April 2019
Contents
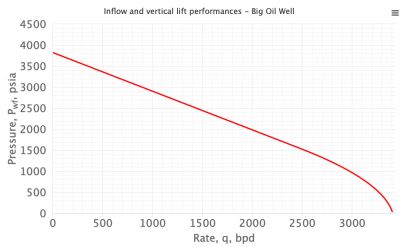
Inflow Performance Relationship
IPR is a curve of producing rates plotted against well bottomhole pressures [1].
IPR curve shows productive capacity and performance of a well.
IPR curve is used in Nodal Analysis for production systems design, analysis and optimization.
Math and Physics
Oil well IPR equation
- Darcy's law inflow equation for the single phase incompressible liquid:
- Vogel IPR two phase equation (liquid + gas)
- Composite IPR
Gas well IPR equation
- Darcy's law gas inflow equation:
- C and n equation
IPR calculator software
- PQplot nodal analysis software is used to calculate the IPR curves. PQplot is available online at www.pengtools.com.
- Excel
- other
Nomenclature
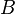 = formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= formation volume factor, bbl/stb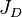 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless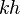 = permeability times thickness, md*ft
= permeability times thickness, md*ft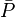 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia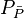 = average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP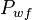 = well flowing pressure, psia
= well flowing pressure, psia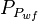 = average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP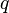 = flowing rate, stb/d
= flowing rate, stb/d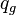 = gas rate, MMscfd
= gas rate, MMscfd = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R
Greek symbols
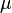 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp