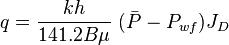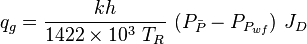Difference between revisions of "IPR"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Oil well IPR equation) |
(→Oil well IPR equation) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*[[Vogel IPR]] two phase equation (oil + gas) | *[[Vogel IPR]] two phase equation (oil + gas) | ||
| − | *[[Composite IPR]] | + | *[[Composite IPR]] three phase equation (oil + gas + water) |
===Gas well IPR equation === | ===Gas well IPR equation === | ||
Revision as of 11:14, 29 March 2019
Contents
Inflow Performance Relationship
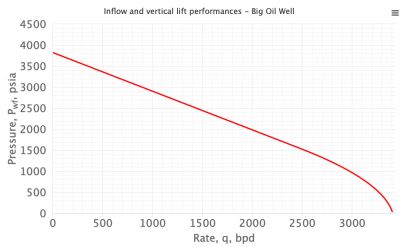
IPR is relationship between well bottomhole pressure and well production rate, usually in a form of a curve.
IPR curve shows productive capacity and performance of a well.
IPR curve is used in Nodal Analysis for production systems design, analysis and optimization.
Math and Physics
Oil well IPR equation
- Darcy's law inflow equation for the single phase liquid:
- Vogel IPR two phase equation (oil + gas)
- Composite IPR three phase equation (oil + gas + water)
Gas well IPR equation
- Darcy's law gas inflow equation:
- C and n equation
IPR calculator software
- PQplot nodal analysis software is used to calculate the IPR curves. PQplot is available online at www.pengtools.com.
- Excel
- other
Nomenclature
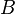 = formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= formation volume factor, bbl/stb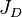 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless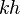 = permeability times thickness, md*ft
= permeability times thickness, md*ft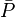 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia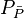 = average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average reservoir pseudopressure, psia2/cP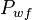 = well flowing pressure, psia
= well flowing pressure, psia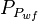 = average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= average well flowing pseudopressure, psia2/cP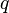 = flowing rate, stb/d
= flowing rate, stb/d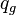 = gas rate, MMscfd
= gas rate, MMscfd = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R
Greek symbols
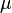 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp