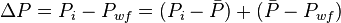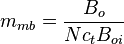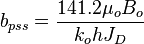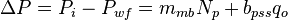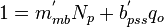Difference between revisions of "Reciprocal Rate Method"
(→Math & Physics) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> B_{o}(P) </math> = oil formation volume factor as a function of pressure, bbl/stb | ||
| + | :<math> J_D </math> = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> {J_D}_{norm} </math> = dimensionless productivity index in terms of the oil pseudo pressure, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> k_oh</math> = oil permeability times thickness, md*ft | ||
| + | :<math> N </math> = stock tank oil initially in place, stb | ||
| + | :<math> {N_p}_{norm} </math> = normalized cumulative oil production, stb | ||
| + | :<math> P </math> = pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> \bar{P} </math> = average reservoir pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> P_{i} </math> = initial pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> P_{po} </math> = oil pseudo pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> P_{ref} </math> = reference pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> P_{wf} </math> = well flowing pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> q_o </math> = oil rate, stb/d | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Greek symbols=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> \mu_o(P) </math> = oil viscosity as a function of pressure, cp | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 20:50, 28 May 2018
Contents
Brief
Reciprocal Rate Method - is the method to estimate oil Wells and Reservoirs EUR using only rate-time production data[1] published in 2007 by Thomas Blasingame et al.
The methodology does presume that flowing well bottomhole pressures are approximately constant[1].
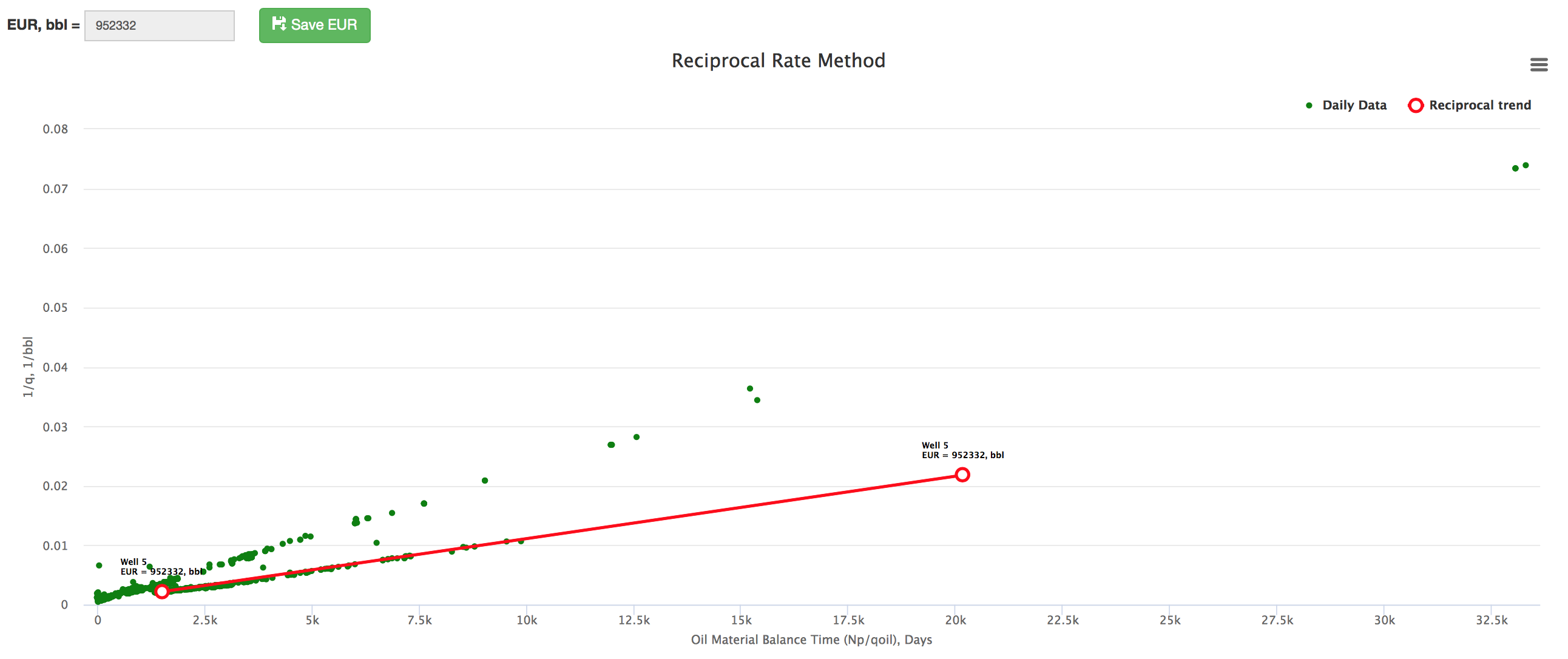
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight line to estimate the slope which gives EUR.
Math & Physics
The total pressure drop at the wellbore is:
Where:
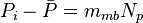 , is pressure drop due to depletion defined by the Oil Material Balance for black oil at P>Pb,
, is pressure drop due to depletion defined by the Oil Material Balance for black oil at P>Pb,
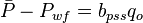 , is pressure drop due to Darcy's law
, is pressure drop due to Darcy's law
Where:
The total pressure drop at the wellbore now can be rewritten as:
Dividing both sides by the assumed constant: 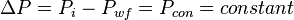 [1]:
[1]:
As the flowrate decreases to zero (i.e., qo → 0)[1]:
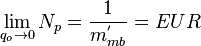
Therefore a plot of 1/qo versus Np/qo yields a straight-line trend where the slope of the line is inversely proportional to the EUR[1].
Discussion
Reciprocal Rate Method can be applied to estimate:
Case Study
This Case Study demonstrates the application of the Oil Flowing Material Balance engineering technique using the E&P Portal.
The Study is based on the oil well from a field in West Siberia, Russia.
It is shown how to:
- Input the data to the E&P Portal;
- Apply the Oil FMB to estimate the well's STOIIP and JD;
- Save and export the analysis results.
All the input data is attached to the Case Study for the reference.
Download the input well production data (csv)
Workflow
- Upload the data required
- Open the Oil Flowing Material Balance tool here
- Estimate the N (red line X-axis intercept)
- Calculate the average reservoir pressure
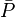 based on N, known production data and using Oil Material Balance equation
based on N, known production data and using Oil Material Balance equation - Calculate the
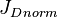
- Calculate the
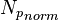
- Plot the orange
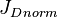 vs
vs 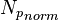 line:
line: - Change the N to match the orange line with the red one
- Change the gray JD line Y-axis intercept to match the changing JD
- Save the Oil Flowing Material Balance model
- Move to the next well
Data required
- Create Field here
- Create or Upload Reservoirs here
- Input the Reservoirs GIIP and STOIIP here
- Create or Upload PVT (SG, Pi, Ti) here
- Upload Wells
- Create or Upload Wells Perforations here
- Create or Upload kh and JD here
- Upload Daily Measures
In case you need to calculate the flowing bottomhole pressure from the wellhead pressure:
- Calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures using BHP Calculator
- Export flowing bottomhole pressures to Daily Measures here
In case you want to add the static reservoir pressures on the FMB Plot:
- Create or Upload the static reservoir pressures, here
- Calculate Monthly Measures from the Daily Measures using Monthly Data Calculator
Nomenclature
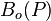 = oil formation volume factor as a function of pressure, bbl/stb
= oil formation volume factor as a function of pressure, bbl/stb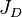 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless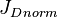 = dimensionless productivity index in terms of the oil pseudo pressure, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index in terms of the oil pseudo pressure, dimensionless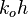 = oil permeability times thickness, md*ft
= oil permeability times thickness, md*ft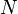 = stock tank oil initially in place, stb
= stock tank oil initially in place, stb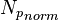 = normalized cumulative oil production, stb
= normalized cumulative oil production, stb = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia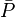 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia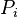 = initial pressure, psia
= initial pressure, psia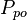 = oil pseudo pressure, psia
= oil pseudo pressure, psia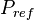 = reference pressure, psia
= reference pressure, psia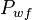 = well flowing pressure, psia
= well flowing pressure, psia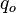 = oil rate, stb/d
= oil rate, stb/d
Greek symbols
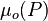 = oil viscosity as a function of pressure, cp
= oil viscosity as a function of pressure, cp