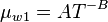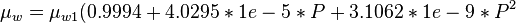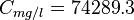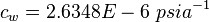Difference between revisions of "Water viscosity"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Water viscosity) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Water viscosity== | ==Water viscosity== | ||
| − | The formation water (brine) isothermal viscosity correlation is published by '''McCain''' in ''' | + | The formation water (brine) isothermal viscosity correlation is published by '''McCain''' in '''1991'''<ref name= M1991/>. |
[[File:Water viscosity.png|thumb|right|400px|Water viscosity <ref name= M1990/>]] | [[File:Water viscosity.png|thumb|right|400px|Water viscosity <ref name= M1990/>]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Math and Physics== | ==Math and Physics== | ||
| − | + | :<math> \mu_{w1} = AT^{-B}</math><ref name= M1991/> | |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> \mu_{w} = \mu_{w1} (0.9994 + 4.0295 * 1e-5 * P + 3.1062 * 1e-9 * P^2</math><ref name= M1991/> |
== Application range == | == Application range == | ||
Revision as of 06:15, 2 October 2020
Contents
Water viscosity
The formation water (brine) isothermal viscosity correlation is published by McCain in 1991[1].
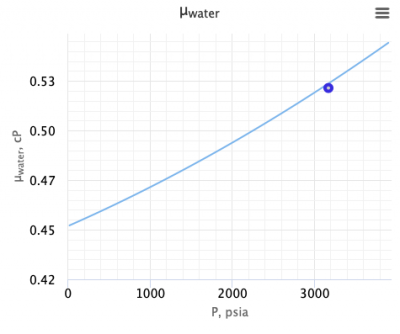
Water viscosity [2]
Math and Physics
Application range
The correlation is valid only for temperatures between 200 and 270F, pressures of 1000 to 20000 psia, and salinities up to 200000 mg/l[1].
Discussion
We, at pengtools.com, are calculating water compressibility below the bubble point with the same equation at the moment.
Example. Calculating water isothermal compressibility
Example source [2]
Input data
Calculate water isothermal compressibility at 3500 psia and 165°F?
Solution
Nomenclature
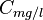 = pressure correction, res bbl/STB
= pressure correction, res bbl/STB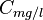 = water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l
= water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia = Temperature, °F
= Temperature, °F
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 McCain, W.D. Jr. (1991). "Reservoir-Fluid Property Correlations-State of the Art"
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-18571-PA).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-18571-PA).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351.