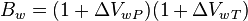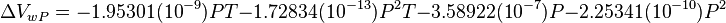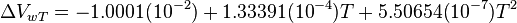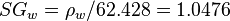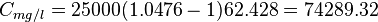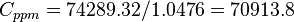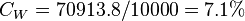Difference between revisions of "Water formation volume factor"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Example. Calculating water salinity from density) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
The correlation is valid through the full range of solids concentrations, temperatures to 260F, and pressures to 5000psia<ref name= M1991/>. | The correlation is valid through the full range of solids concentrations, temperatures to 260F, and pressures to 5000psia<ref name= M1991/>. | ||
| − | ==Example. Calculating water | + | ==Example. Calculating water formation volume factor== |
Example source <ref name= M1990/> | Example source <ref name= M1990/> | ||
===Input data=== | ===Input data=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | Calculate water | + | Calculate water formation volume factor at 3161 psig and 165F? |
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
Revision as of 06:04, 1 October 2020
Contents
Water formation volume factor
The water formation volume factor represents the change in volume of the brine as it is transported from the reservoir conditions to surface conditions[1].
The units are reservoir barrels per surface barrel at standard conditions, res bbl/STB.
Math and Physics
where
Application range
The correlation is valid through the full range of solids concentrations, temperatures to 260F, and pressures to 5000psia[2].
Example. Calculating water formation volume factor
Example source [1]
Input data
Calculate water formation volume factor at 3161 psig and 165F?
Solution
Nomenclature
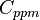 = water salinity / solids concentration, ppm
= water salinity / solids concentration, ppm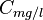 = water salinity / solids concentration, mg/l
= water salinity / solids concentration, mg/l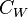 = weight percent solids, %
= weight percent solids, %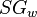 = water specific gravity, dimensionless
= water specific gravity, dimensionless
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351.
- ↑ McCain, W.D. Jr. (1991). "Reservoir-Fluid Property Correlations-State of the Art"
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-18571-PA).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-18571-PA).