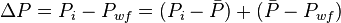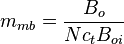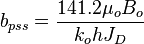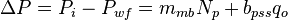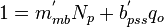Reciprocal Rate Method
Contents
Brief
Reciprocal Rate Method is the method to estimate oil Wells and Reservoirs EUR using only rate-time production data[1] published in 2007 by Thomas Blasingame et al.
The methodology does presume that flowing well bottomhole pressures are approximately constant[1].
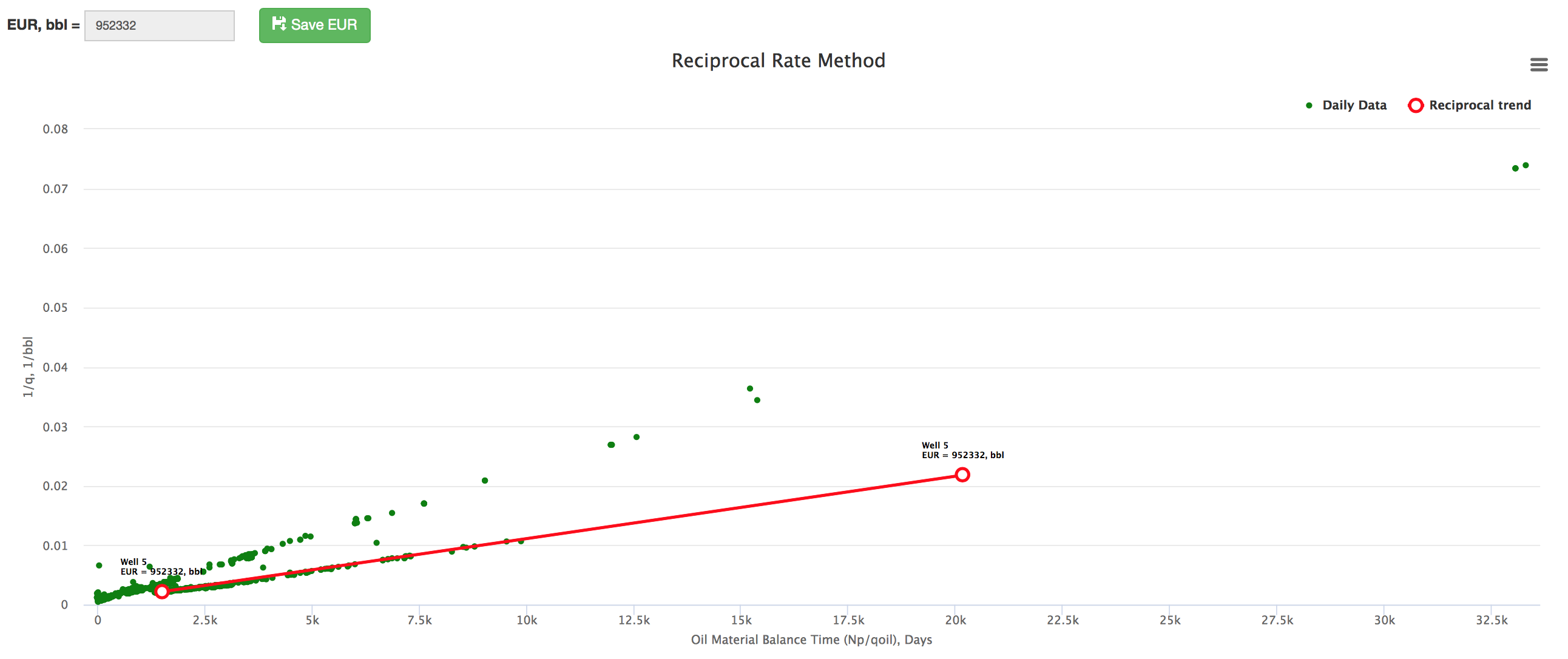
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight line to estimate the slope which gives EUR.
Math & Physics
The total pressure drop at the wellbore is:
Where:
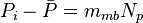 , is pressure drop due to depletion defined by the Oil Material Balance for black oil at P>Pb,
, is pressure drop due to depletion defined by the Oil Material Balance for black oil at P>Pb,
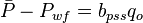 , is pressure drop due to Darcy's law
, is pressure drop due to Darcy's law
Where:
The total pressure drop at the wellbore now can be rewritten as:
Dividing both sides by the assumed constant: 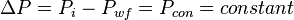 [1]:
[1]:
As the flowrate decreases to zero (i.e., qo → 0)[1]:
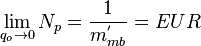
Therefore a plot of 1/qo versus Np/qo yields a straight-line trend where the slope of the line is inversely proportional to the EUR[1].
Discussion
Reciprocal Rate Method can be applied to estimate:
Reciprocal Rate Method can be used for fracture and refracture analysis, sidetrack analysis etc.
E&P Portal has the capability to automatically calculate EUR for a number of Wells or Reservoirs through the EUR calculator.
Examples
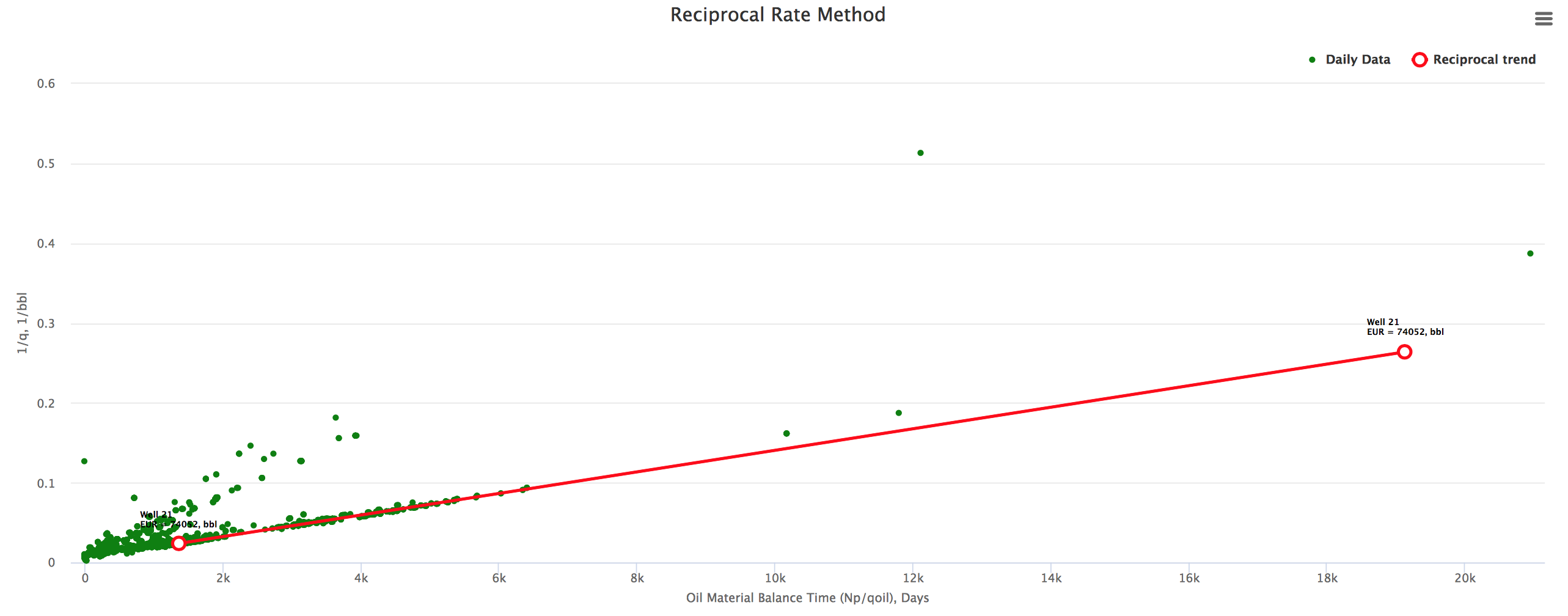
Example 1. Well "21" refrac doubles the EUR as indicated by the slope change.
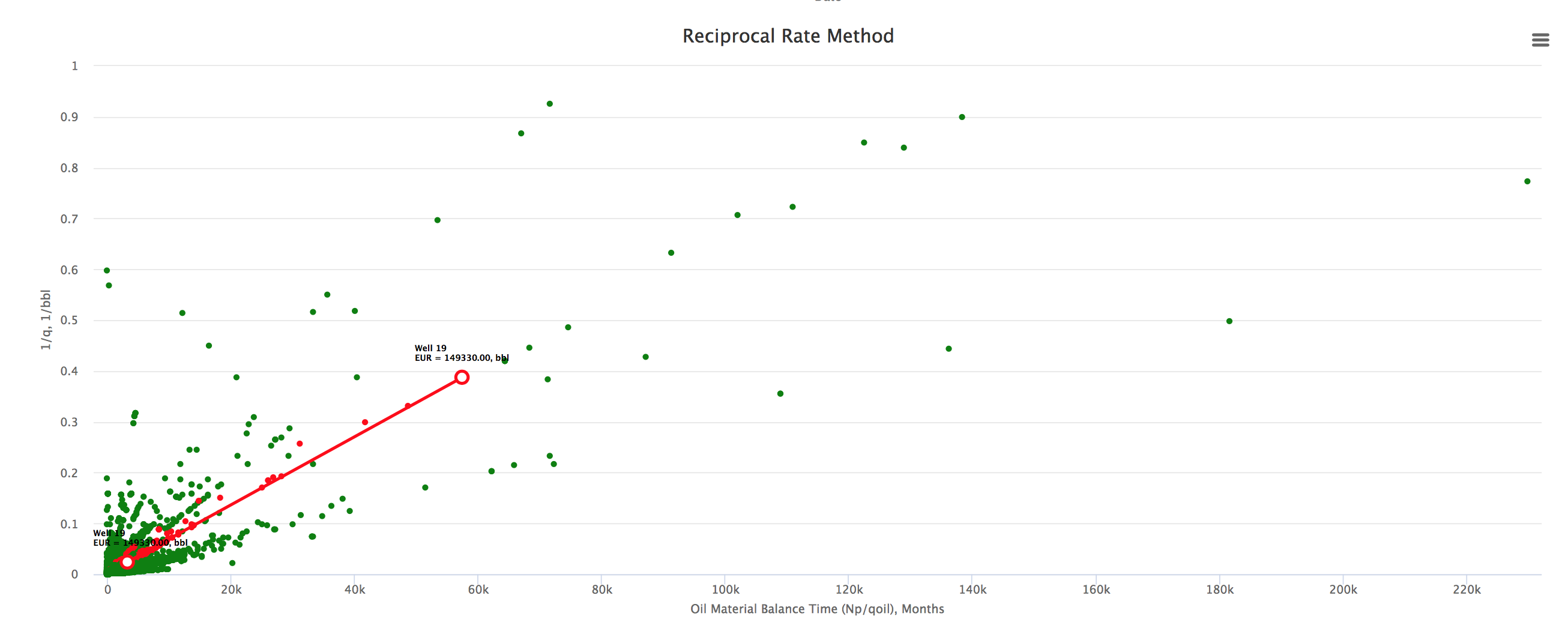
Example 2. 22 wells on the Reciprocal Rate Method plot showing the well's EUR spread. Well "19" trend is highlighted.
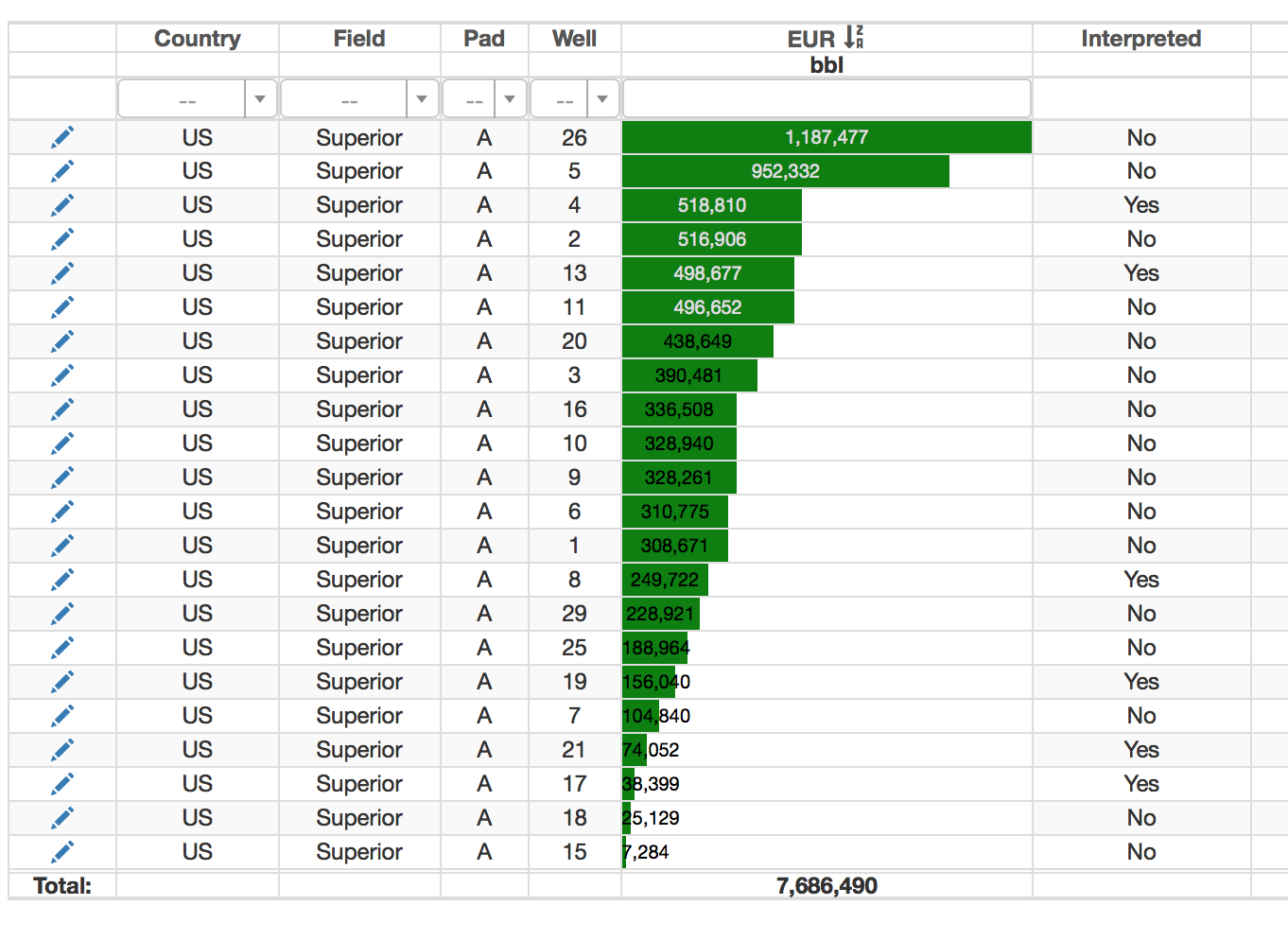
Example 3. EUR results table for 22 wells. Automatically interpreted wells have "No" flag, manually interpreted "Yes" flag in the last column.
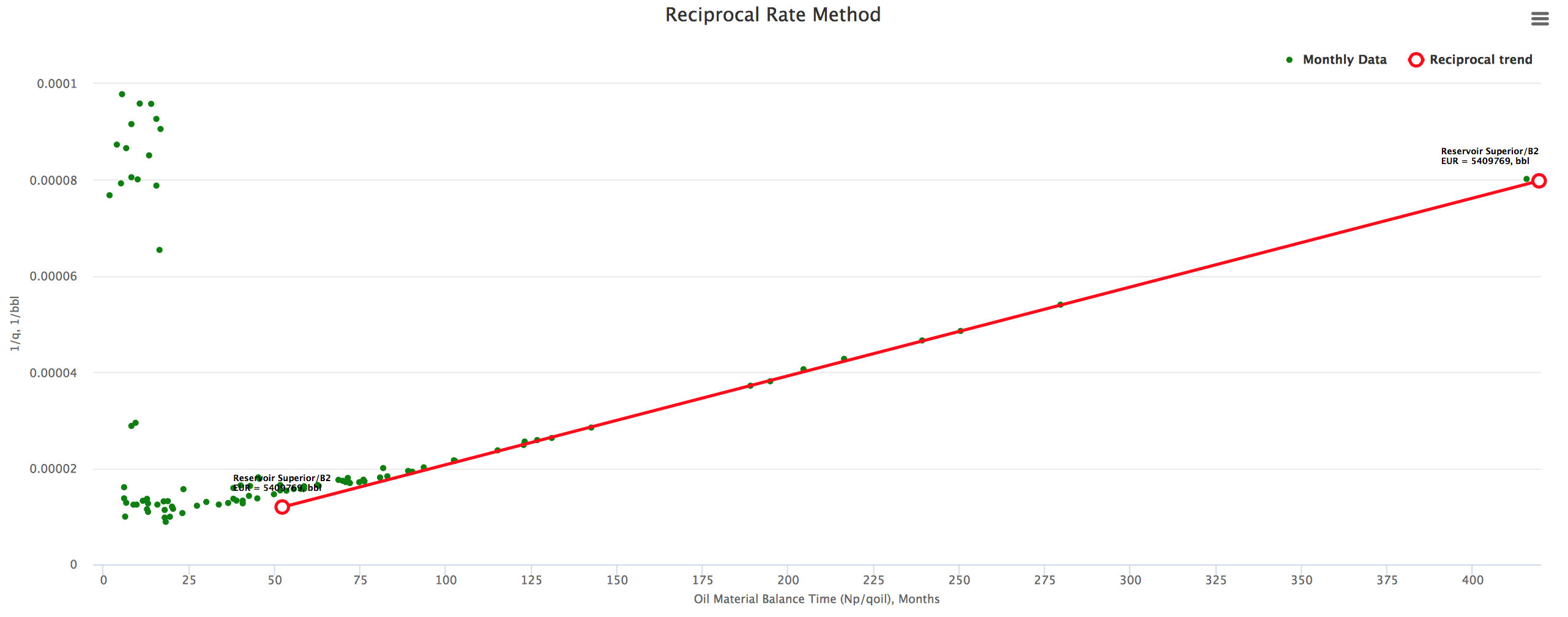
Example 4. "B2" reservoir Reciprocal Rate Method plot showing the Reservoir EUR.
Workflow
- Upload the data required
- Open the Reciprocal Rate Method tool
- Wells tool here
- Reservoirs tool here
- Fit data with the red trend line
- Calculate the slope of the line and EUR
- Save the Reciprocal Rate Method model
- Move to the next Well / Reservoir
Data required
Wells interpretation:
Reservoirs interpretation:
- Create or Upload Reservoirs here
- Upload Perforations to connect Wells to the Reservoirs
Nomenclature
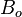 = oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb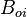 = initial oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb
= initial oil formation volume factor, bbl/stb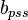 = reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia/stb/d
= reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia/stb/d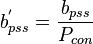 = reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, 1/stb/d
= reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, 1/stb/d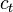 = total compressibility, psia-1
= total compressibility, psia-1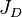 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless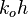 = oil permeability times thickness, md*ft
= oil permeability times thickness, md*ft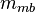 = slope term, psia/stb
= slope term, psia/stb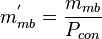 = slope term, 1/stb
= slope term, 1/stb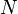 = stock tank oil initially in place, stb
= stock tank oil initially in place, stb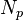 = cumulative oil production, stb
= cumulative oil production, stb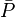 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia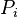 = initial pressure, psia
= initial pressure, psia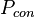 = constant, psia
= constant, psia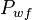 = well flowing pressure, psia
= well flowing pressure, psia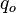 = oil rate, stb/d
= oil rate, stb/d
Greek symbols
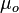 = oil viscosity , cp
= oil viscosity , cp