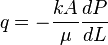Darcy's law
From wiki.pengtools.com
Contents
Darcy's law
Darcy's law is the fundamental law of fluid motion in porous media published by Henry Darcy in 1856 [1].
Darcy's law has been applied successfully to determine the flow through permeable media since the early days of Petroleum Engineering.
Darcy's law History
Henry Darcy worked on the design of a filter large enough to process the Dijon towns daily water requirement [2].
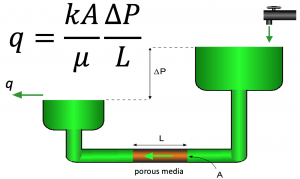
By flowing water through the sand pack Darcy established that, for any flow rate, the velocity of the flow was directly proportional to the difference in manometric heights[2]:
Darcy's law Equation
Conditions
- Single fluid
- Steady stay flow
- Constant fluid compressibility
- Constant temperature
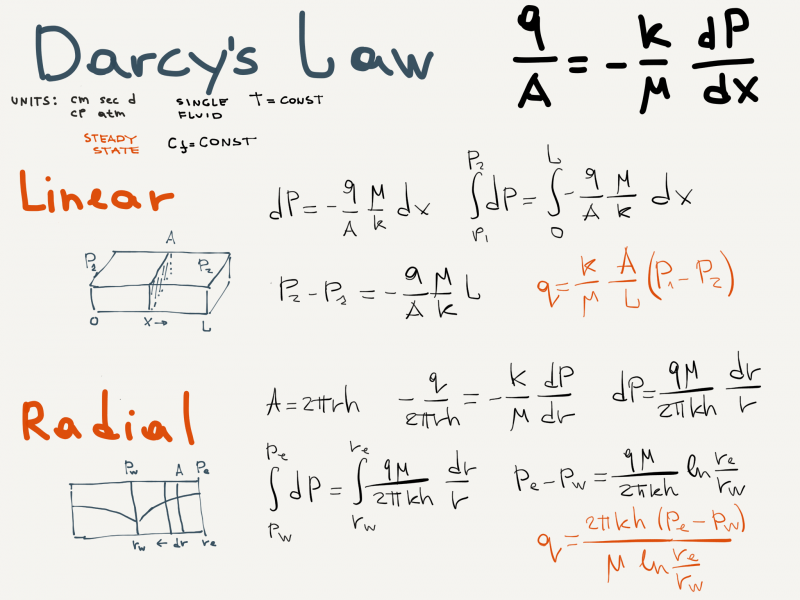
Inflow Equations Derivation
Derivation of the Linear and Radial Inflow Equations
Nomenclature
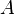 = cross-sectional area, cm2
= cross-sectional area, cm2 = permeability, d
= permeability, d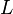 = length, cm
= length, cm = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm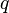 = flow rate, cm3/sec
= flow rate, cm3/sec
Greek symbols
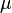 = Darcy's law fluid viscosity, cp
= Darcy's law fluid viscosity, cp
See Also
Darcy's law application in Petroleum Engineering Technology.
References
- ↑ Darcy, Henry (1856). "Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon". Paris: Victor Dalmont.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Dake, L.P. (1978). Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering. Amsterdam, Hetherlands: Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-444-41830-X.