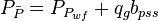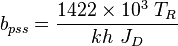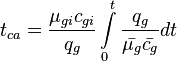Difference between revisions of "Gas Flowing Material Balance"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Nomenclature) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
:<math> P_P </math> = pseudopressure, psai<sup>2</sup>/cP | :<math> P_P </math> = pseudopressure, psai<sup>2</sup>/cP | ||
:<math> q_g </math> = gas rate, MMscfd | :<math> q_g </math> = gas rate, MMscfd | ||
| + | :<math> t </math> = time, day | ||
:<math> t_{ca} </math> = material balance pseudotime for gas, day | :<math> t_{ca} </math> = material balance pseudotime for gas, day | ||
:<math> T </math> = temperature, °R | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °R | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 11 December 2017
Contents
Brief
Gas Flowing Material Balance is the advanced engineering technique to determine the Reservoirs GIIP and recovery as well as Well's EUR and JD.
Gas Flowing Material Balance is applied on the Well level given readily available well flowing data: production rate and tubing head pressure.
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight line to estimate GIIP and JD.
Math & Physics
Combining the gas pseudo state flow equation and the Gas Material Balance equation to get Gas Flowing Material Balance equation:
where
Material balance pseudo-time:
Discussion
well vs reservoir model start
Workflow
- Calculate the red
 line:
line:
- Given the GIIP
- Calculate the
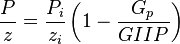
- Calculate the orange
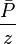 curve:
curve:
- Given the flowing wellhead pressures, calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures,
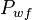
- Convert the flowing pressures to pseudopressures,
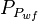
- Given the JD, calculate the
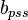
- Calculate the pseudopressure,
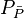
- Convert the pseudopressure to pressure,
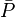
- Calculate the
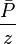
- Given the flowing wellhead pressures, calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures,
- Calculate the gray JD curve:
- Calculate the gas productivity index,
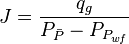
- Calculate the JD,
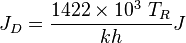
- Calculate the gas productivity index,
- Change the red
 line to match the orange
line to match the orange  curve
curve
- Change the GIIP
- Change the intitial
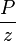
- Change the flat JD gray line to match the changing JD gray line
- Save the Gas Flowing Material Balance model
- Move to the next well
Extra Plot to find bpss
- Calculate the initial pseudopressure,
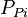
- Calculate the material balance pseudo-time,
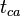
- Plot
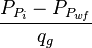 versus
versus 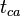
- The intercept with the Y axis gives
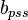 and
and 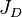
Data required
- Create Field here
- Upload Wells here
- Upload Daily Measures here
- Create or Upload Reservoirs here
- Create or Upload PVT (SG, Pi, Ti) here
- Create or Upload Wells Perforations here
- Create or Upload kh and JD here
- Create or Upload the static reservoir pressures, here
- Export static reservoir pressures to Daily Measures here
- Calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures using BHP Calculator
- Export flowing bottomhole pressures to Daily Measures here
Nomenclature
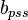 = reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia2/cP/MMscfd
= reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia2/cP/MMscfd = compressibility, psia-1
= compressibility, psia-1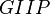 = gas initially in place, MMscf
= gas initially in place, MMscf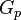 = cumulative gas produced, MMscf
= cumulative gas produced, MMscf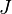 = gas productivity index, MMscfd/(psia2/cP)
= gas productivity index, MMscfd/(psia2/cP)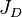 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless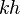 = permeability times thickness, md*m
= permeability times thickness, md*m = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia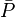 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia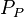 = pseudopressure, psai2/cP
= pseudopressure, psai2/cP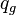 = gas rate, MMscfd
= gas rate, MMscfd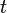 = time, day
= time, day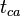 = material balance pseudotime for gas, day
= material balance pseudotime for gas, day = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R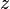 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
Greek symbols
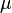 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp
Subscripts
- g = gas
- i = initial
- K = °K
- R = °R
- wf = well flowing
References
- ↑ Mattar, L.; Anderson, D (2005). "Dynamic Material Balance (Oil or Gas-In-Place Without Shut-Ins)" (PDF). CIPC.