Difference between revisions of "Decline Curve Analysis"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math & Physics) |
(→Math & Physics) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Math & Physics == | == Math & Physics == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<table width="100%" border="1" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="1"> | <table width="100%" border="1" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="1"> | ||
| Line 22: | Line 17: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td>General form equation <ref name = DDA/></td> | <td>General form equation <ref name = DDA/></td> | ||
| − | <td> | + | <td><math>q(t) = \frac{q_i}{(1+b\ D_i\ t)^{1/b}}</math></td> |
| − | <td> | + | <td><math> Q = \frac{q^b_i}{D_i\ (1-b)} (q^{1-b}_i-q(t)^{1-b})</math></td> |
</tr> | </tr> | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 26 October 2017
Contents
Brief
Decline Curve Analysis DCA is an empirical method for rate decline analysis and rate forecasting published by Arps in 1945 [1].
DCA is applied for Wells and Reservoirs production forecasting.
Math & Physics
| Note | Rate | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| General form equation [2] | 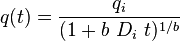 |
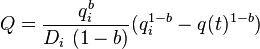 |
| Gas-oil ratio | Velarde | Velarde, J., Blasingame, T.A., and McCain Jr., W.D. 1997. Correlation of Black Oil Properties At Pressures Below Bubble Point Pressure - A New Approach. Presented at the Annual Technical Meeting of CIM, Calgary, Alberta, 8–11 June. PETSOC-97-93. |
References
- ↑ Arps, J. J. (1945). "Analysis of Decline Curves"
 . Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 160 (01).
. Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 160 (01).
- ↑ "KAPPA Dynamic Data Analysis (DDA) book"
 .
.
