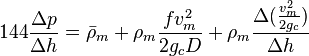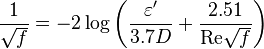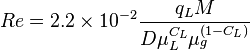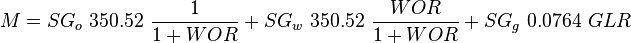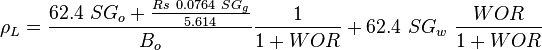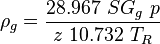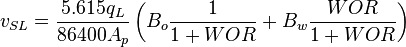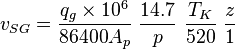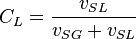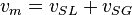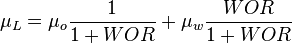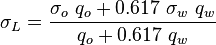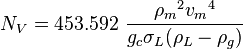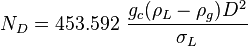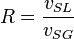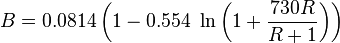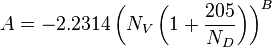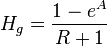Difference between revisions of "Gray correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→References) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
NV velocity number | NV velocity number | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> B </math> = correlation group, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> B </math> = formation factor, bbl/stb | ||
| + | :<math> C </math> = coefficient for liquid viscosity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> D </math> = pipe diameter, ft | ||
| + | :<math> h </math> = depth, ft | ||
| + | :<math> H </math> = correlation group, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> H_L </math> = liquid holdup factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> f </math> = friction factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> GLR </math> = gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> M </math> = total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lb<sub>m</sub>/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> N_D </math> = pipe diameter number number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_GV </math> = gas velocity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_L </math> = liquid viscosity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_LV </math> = liquid velocity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> p </math> = pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> q_c </math> = conversion constant equal to 32.174, lb<sub>m</sub>ft / lb<sub>f</sub>sec<sup>2</sup> | ||
| + | :<math> q_L </math> = total liquid production rate, bbl/d | ||
| + | :<math> Re </math> = Reynolds number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb | ||
| + | :<math> SG </math> = specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript | ||
| + | :<math> v </math> = velocity, ft/sec | ||
| + | :<math> WOR </math> = water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Greek symbols=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> \varepsilon </math> = absolute roughness, ft | ||
| + | :<math> \mu </math> = oil viscosity, cp | ||
| + | :<math> \rho </math> = density, lb<sub>m</sub>/ft<sup>3</sup> | ||
| + | :<math> \bar \rho </math> = integrated average density at flowing conditions, lb<sub>m</sub>/ft<sup>2</sup> | ||
| + | :<math> \sigma </math> = surface tension of liquid-air interface, dynes/cm (ref. values: 72 - water, 35 - oil) | ||
| + | :<math> \psi </math> = secondary correlation factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Subscripts=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | g = gas<BR/> | ||
| + | K = °K<BR/> | ||
| + | L = liquid<BR/> | ||
| + | m = gas/liquid mixture<BR/> | ||
| + | o = oil<BR/> | ||
| + | R = °R<BR/> | ||
| + | SL = superficial liquid<BR/> | ||
| + | SG = superficial gas<BR/> | ||
| + | w = water<BR/> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 6 April 2017
Contents
Brief
Gray is an empirical two-phase flow correlation published in 1974 [1].
Gray is the default VLP correlation for the gas wells in the PQplot.
Math & Physics
Following the law of conservation of energy the basic steady state flow equation is:
where
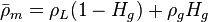 , slip mixture density
, slip mixture density
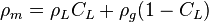 , no-slip mixture density
, no-slip mixture density
Colebrook–White [2] equation for the Darcy's friction factor:
The pseudo wall roughness:
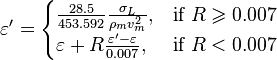 , with the limit
, with the limit 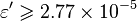 [1]
[1]
Reynolds two phase number:
Discussion
Why Gray correlation?
The Gray correlation was found to be the best of several initially tested ...— Nitesh Kumar l[5]
Workflow Hg & CL
Modifications
use watercut instead of WOR
Nomenclature
NV velocity number
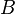 = correlation group, dimensionless
= correlation group, dimensionless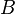 = formation factor, bbl/stb
= formation factor, bbl/stb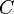 = coefficient for liquid viscosity number, dimensionless
= coefficient for liquid viscosity number, dimensionless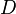 = pipe diameter, ft
= pipe diameter, ft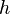 = depth, ft
= depth, ft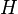 = correlation group, dimensionless
= correlation group, dimensionless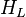 = liquid holdup factor, dimensionless
= liquid holdup factor, dimensionless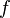 = friction factor, dimensionless
= friction factor, dimensionless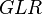 = gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl
= gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl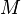 = total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl
= total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl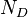 = pipe diameter number number, dimensionless
= pipe diameter number number, dimensionless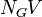 = gas velocity number, dimensionless
= gas velocity number, dimensionless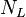 = liquid viscosity number, dimensionless
= liquid viscosity number, dimensionless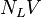 = liquid velocity number, dimensionless
= liquid velocity number, dimensionless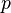 = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia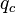 = conversion constant equal to 32.174, lbmft / lbfsec2
= conversion constant equal to 32.174, lbmft / lbfsec2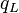 = total liquid production rate, bbl/d
= total liquid production rate, bbl/d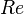 = Reynolds number, dimensionless
= Reynolds number, dimensionless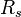 = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb
= solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb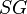 = specific gravity, dimensionless
= specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript
= temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript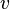 = velocity, ft/sec
= velocity, ft/sec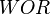 = water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl
= water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl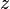 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
Greek symbols
 = absolute roughness, ft
= absolute roughness, ft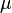 = oil viscosity, cp
= oil viscosity, cp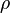 = density, lbm/ft3
= density, lbm/ft3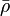 = integrated average density at flowing conditions, lbm/ft2
= integrated average density at flowing conditions, lbm/ft2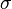 = surface tension of liquid-air interface, dynes/cm (ref. values: 72 - water, 35 - oil)
= surface tension of liquid-air interface, dynes/cm (ref. values: 72 - water, 35 - oil)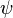 = secondary correlation factor, dimensionless
= secondary correlation factor, dimensionless
Subscripts
g = gas
K = °K
L = liquid
m = gas/liquid mixture
o = oil
R = °R
SL = superficial liquid
SG = superficial gas
w = water
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Gray, H. E. (1974). "Vertical Flow Correlation in Gas Wells". User manual for API 14B, Subsurface controlled safety valve sizing computer program. API.
- ↑ Colebrook, C. F. (1938–1939). "Turbulent Flow in Pipes, With Particular Reference to the Transition Region Between the Smooth and Rough Pipe Laws"
 . Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
. Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
- ↑ Moody, L. F. (1944). "Friction factors for pipe flow"
 . Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
. Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hagedorn, A. R.; Brown, K. E. (1965). "Experimental study of pressure gradients occurring during continuous two-phase flow in small-diameter vertical conduits". Journal of Petroleum Technology. 17(04): 475–484.
- ↑ Kumar, N.; Lea, J. F. (January 1, 2005). "Improvements for Flow Correlations for Gas Wells Experiencing Liquid Loading"
 (SPE-92049-MS).
(SPE-92049-MS).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Lyons, W.C. (1996). Standard handbook of petroleum and natural gas engineering. 2. Houston, TX: Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 0-88415-643-5.