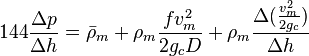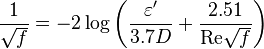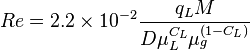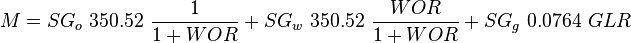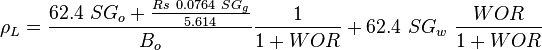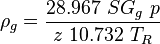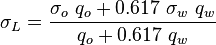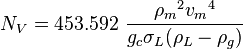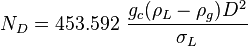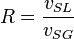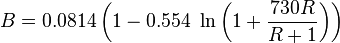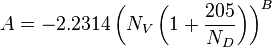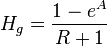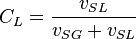Difference between revisions of "Gray correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→References) |
(→References) |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
|volume=17(04) | |volume=17(04) | ||
|pages=475-484 | |pages=475-484 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ref name= Lyons>{{cite book | ||
| + | |last1= Lyons |first1=W.C. | ||
| + | |title=Standard handbook of petroleum and natural gas engineering | ||
| + | |date= 1996 | ||
| + | |volume=2 | ||
| + | |publisher=Gulf Professional Publishing | ||
| + | |place=Houston, TX | ||
| + | |isbn=0-88415-643-5 | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:15, 4 April 2017
Brief
Math & Physics
Following the law of conservation of energy the basic steady state flow equation is:
where
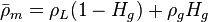 , slip mixture density
, slip mixture density
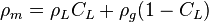 , no-slip mixture density
, no-slip mixture density
Colebrook–White [2] equation for the Darcy's friction factor:
The pseudo wall roughness [1]:
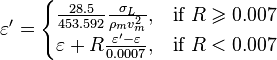 , with the limit
, with the limit 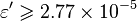
Reynolds two phase number:
Discussion
Workflow Hg
Nomenclature
NV velocity number
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Gray, H. E. (1974). "Vertical Flow Correlation in Gas Wells". User manual for API 14B, Subsurface controlled safety valve sizing computer program. API.
- ↑ Colebrook, C. F. (1938–1939). "Turbulent Flow in Pipes, With Particular Reference to the Transition Region Between the Smooth and Rough Pipe Laws"
 . Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
. Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
- ↑ Moody, L. F. (1944). "Friction factors for pipe flow"
 . Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
. Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
- ↑ Hagedorn, A. R.; Brown, K. E. (1965). "Experimental study of pressure gradients occurring during continuous two-phase flow in small-diameter vertical conduits". Journal of Petroleum Technology. 17(04): 475–484.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Lyons, W.C. (1996). Standard handbook of petroleum and natural gas engineering. 2. Houston, TX: Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 0-88415-643-5.