Difference between revisions of "PQplot"
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
<tr><td> | <tr><td> | ||
| − | Liquid loading | + | [[Liquid loading]] |
</td><td> | </td><td> | ||
Turner | Turner | ||
Revision as of 11:46, 15 March 2017
Contents
Short Description
PQplot tool allows to perform System analysis (or Nodal analysis) of oil and gas wells. System analysis may be used for many purposes in analyzing and designing producing wells.
Typical applications include
- Estimation of flow rates
- Selection of tubing size
- Selection of flowline size
- Selection of wellhead pressures and surface choke sizing
- Estimation of the effects of reservoir pressure depletion
- Identification of flow restrictions
Main features
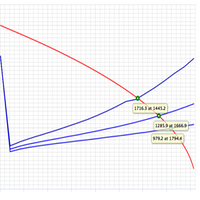
- Plot of Inflow performance curve (IPR) and Vertical lift performance curve (VLP)
- Rate and pressure at intersection point
- Sensitivity analysis of IPR and VLP curves on parameters
- Using prepared PVT models
- Inclined wells calculations
- Tubing, annular and both flow types
Interface features
- Save and share references to saved models with colleagues
- Last saved model on current computer and browser is automatically opened
- Choose between Metric units and US oilfield units
- Save as image and print plot by means of chart context menu (button at the upper-right corner of chart)
- Download report in pdf format containing input parameters, calculated values and plot
- Select and copy results to Excel or other application
Used correlations
| Type of problem | Correlation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Oil well vertical lift |
Hagedorn, A. R., & Brown, K. E. (1965). Experimental study of pressure gradients occurring during continuous two-phase flow in small-diameter vertical conduits. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 17(04), 475-484. | |
|
Gas well vertical lift |
Gray |
Gray, H. E. (1974). Vertical flow correlation in gas wells. User manual for API14B, subsurface controlled safety valve sizing computer program. |
|
Gas well with zero oil-gas ratio vertical lift |
Multi-step Cullender and Smith |
Cullender, M.H. and Smith, R.V. 1956. Practical Solution of Gas-Flow Equations for Wells and Pipelines with Large Temperature Gradients. Trans., AIME 207: 281. |
|
Oil well inflow |
Composite IPR based – Vogel equations taking into account water |
Kermit E. Brown "The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods" Vol. 4 Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis, p. 30, section 2.227.1 |
|
Gas well inflow – backpressure equation |
Rawlins and Schellhardt |
Rawlins, E.L. and Schellhardt, M.A. 1935. Backpressure Data on Natural Gas Wells and Their Application to Production Practices, Vol. 7. Monograph Series, USBM. |
|
Gas well inflow – pseudo-pressure equation using Jd and kh values |
Real-gas pseudopressure equation |
See for example: Ahmed, T., & McKinney, P. (2011). Advanced reservoir engineering. Gulf Professional Publishing. |
|
Turner |
Turner, R. G., Hubbard, M. G., and Dukler, A. E. (1969) “Analysis and Prediction of Minimum Flow Rate for the Continuous Removal of Liquids from Gas Wells,” Journal of Petroleum Technology, Nov. 1969. pp. 1475–1482. | |
|
Erosional velocity |
Guidelines from API RP14E |
Mokhatab S, Poe WA, Speight JG (2006) "Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing", Section 11.6 - Design Considerations on sales gas pipelines, subsection 11.6.1 - Line Sizing Criteria, Elsevier, 2006. |
PVT correlations are the same as in PVT calculator.