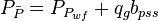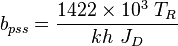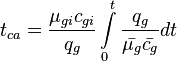Difference between revisions of "Gas Flowing Material Balance"
(→Brief) |
(→Brief) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Brief == | == Brief == | ||
| − | [[Gas Flowing Material Balance]] '''(FMB)''' is the advanced engineering technique to determine | + | [[Gas Flowing Material Balance]] '''(FMB)''' is the advanced engineering technique to determine |
| + | * [[Reservoirs]] GIIP & [[EUR]] | ||
| + | * [[Well]]'s [[EUR]] and [[JD]]. | ||
[[Gas Flowing Material Balance]] is applied on the [[Well]] level given readily available well flowing data: production rate and tubing head pressure. | [[Gas Flowing Material Balance]] is applied on the [[Well]] level given readily available well flowing data: production rate and tubing head pressure. | ||
Revision as of 12:18, 12 December 2017
Contents
Brief
Gas Flowing Material Balance (FMB) is the advanced engineering technique to determine
- Reservoirs GIIP & EUR
- Well's EUR and JD.
Gas Flowing Material Balance is applied on the Well level given readily available well flowing data: production rate and tubing head pressure.
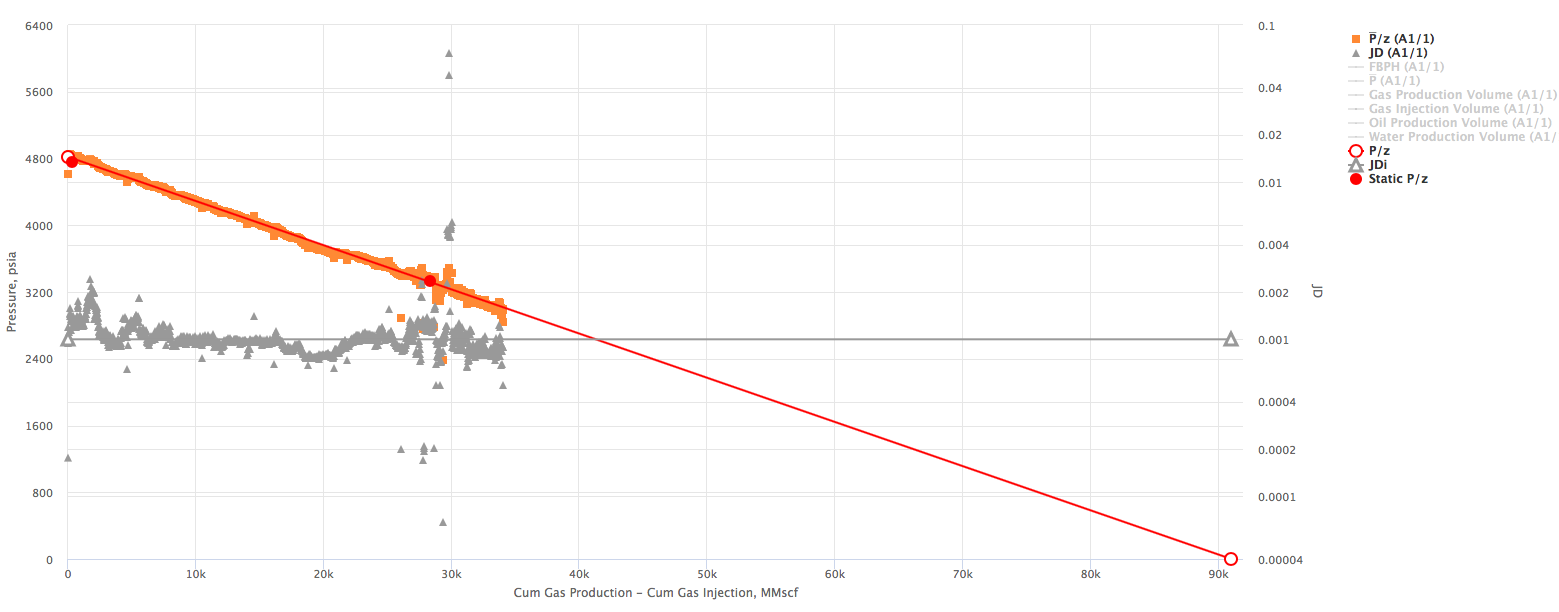
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight lines to estimate GIIP and JD.
Math & Physics
Combining the gas pseudo state flow equation and the Gas Material Balance equation to get Gas Flowing Material Balance equation:
where
Material balance pseudo-time:
Discussion
Gas Flowing Material Balance can be applied to:
- single well
- multiple wells producing from the same Reservoir.
The X axis on the Gas Flowing Material Balance Plot can be selected as:
Example 1. Multiple wells producing from the same Reservoir. X axis - Wells cumulative
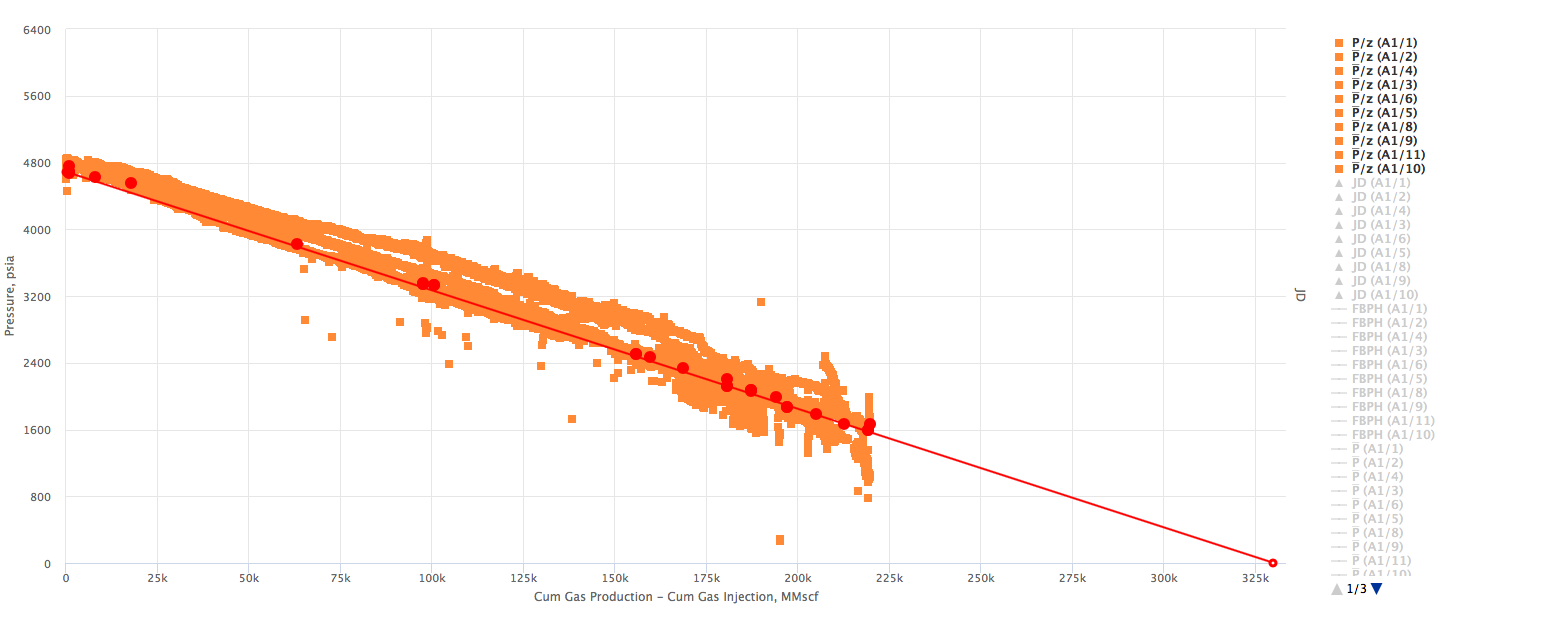
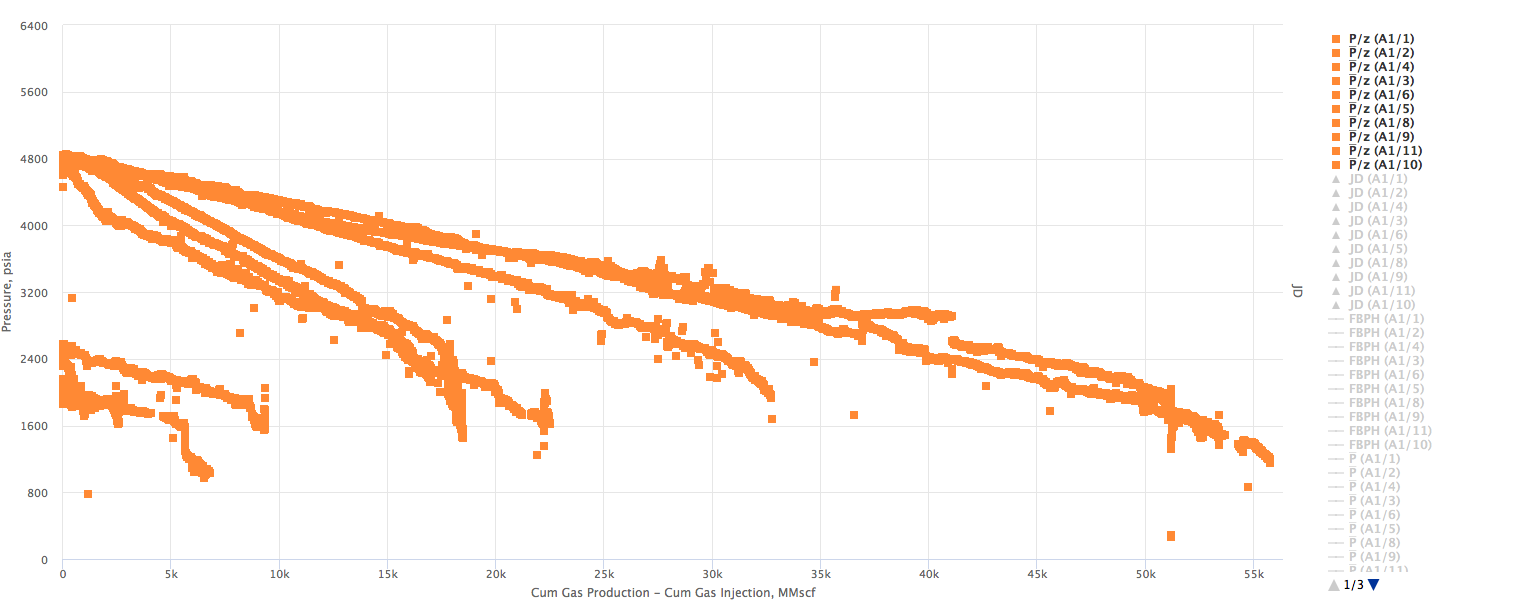 Example 2. Multiple wells producing from the same Reservoir. X axis - Reservoir cumulative
Example 2. Multiple wells producing from the same Reservoir. X axis - Reservoir cumulative
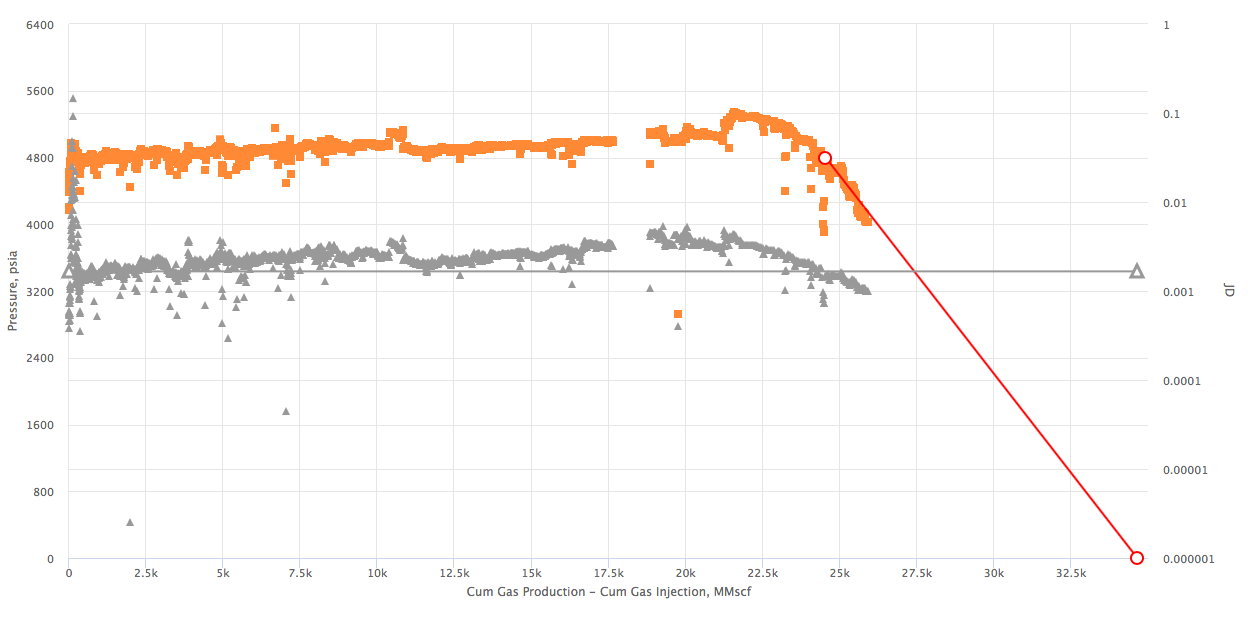
 Example 3. Shifted Model Start (to account for gas injection)
Example 3. Shifted Model Start (to account for gas injection)
Workflow
- Upload the data required
- Open the Gas Flowing Material Balance tool here
- Calculate the red
 line:
line:
- Given the GIIP
- Calculate the
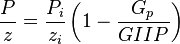
- Calculate the orange
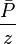 curve:
curve:
- Given the flowing wellhead pressures, calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures,
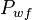
- Convert the flowing pressures to pseudopressures,
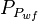
- Given the JD, calculate the
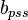
- Calculate the pseudopressure,
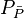
- Convert the pseudopressure to pressure,
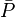
- Calculate the
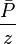
- Given the flowing wellhead pressures, calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures,
- Calculate the gray JD curve:
- Calculate the gas productivity index,
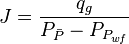
- Calculate the JD,
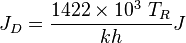
- Calculate the gas productivity index,
- Change the red
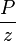 line to match the orange
line to match the orange 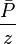 curve
curve
- Change the GIIP
- Change the intitial
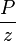
- Change the flat JD gray line to match the changing JD gray line
- Save the Gas Flowing Material Balance model
- Move to the next well
Extra Plot to find bpss
- Calculate the initial pseudopressure,
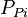
- Calculate the material balance pseudo-time,
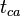
- Plot
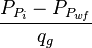 versus
versus 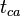
- The intercept with the Y axis gives
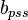 and
and 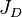
Data required
- Create Field here
- Upload Wells here
- Upload Daily Measures here
- Create or Upload Reservoirs here
- Input the Reservoirs GIIP here
- Create or Upload PVT (SG, Pi, Ti) here
- Create or Upload Wells Perforations here
- Create or Upload kh and JD here
- Create or Upload the static reservoir pressures, here
- Export static reservoir pressures to Daily Measures here
- Calculate the flowing bottomhole pressures using BHP Calculator
- Export flowing bottomhole pressures to Daily Measures here
Nomenclature
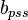 = reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia2/cP/MMscfd
= reservoir constant, inverse to productivity index, psia2/cP/MMscfd = compressibility, psia-1
= compressibility, psia-1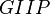 = gas initially in place, MMscf
= gas initially in place, MMscf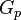 = cumulative gas produced, MMscf
= cumulative gas produced, MMscf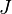 = gas productivity index, MMscfd/(psia2/cP)
= gas productivity index, MMscfd/(psia2/cP)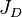 = dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless
= dimensionless productivity index, dimensionless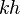 = permeability times thickness, md*m
= permeability times thickness, md*m = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia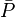 = average reservoir pressure, psia
= average reservoir pressure, psia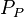 = pseudopressure, psia2/cP
= pseudopressure, psia2/cP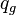 = gas rate, MMscfd
= gas rate, MMscfd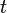 = time, day
= time, day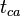 = material balance pseudotime for gas, day
= material balance pseudotime for gas, day = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R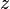 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
Greek symbols
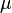 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp
Subscripts
- g = gas
- i = initial
- R = °R
- wf = well flowing
References
- ↑ Mattar, L.; Anderson, D (2005). "Dynamic Material Balance (Oil or Gas-In-Place Without Shut-Ins)" (PDF). CIPC.