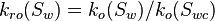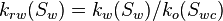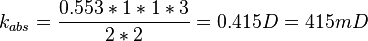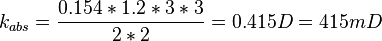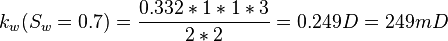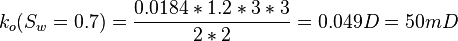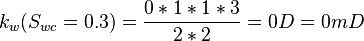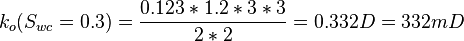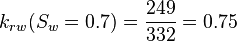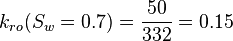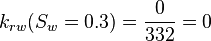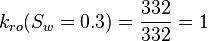Difference between revisions of "Relative Permeability"
(→Brief) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Brief== | ==Brief== | ||
| − | [[Relative Permeability]] is the ratio of the effective permeability to base oil permeability measured at connate water saturation. | + | [[Relative Permeability]] is the ratio of the effective permeability to base oil permeability measured at connate water saturation<ref name=DW/>. |
| − | :<math> k_{ro} = k_o/ | + | :<math> k_{ro}(S_w) = k_o(S_w)/k_o(S_{wc})</math> |
| − | :<math> k_{rw} = k_w/ | + | |
| + | :<math> k_{rw}(S_w) = k_w(S_w)/k_o(S_{wc})</math> | ||
where | where | ||
| − | :<math> k_{ro} =</math> Oil relative permeability, fraction | + | :<math> k_{ro}(S_w) =</math> Oil relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction |
| − | :<math> k_{rw} =</math> Water relative permeability, fraction | + | :<math> k_{rw}(S_w) =</math> Water relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction |
| − | :<math> k_o =</math> Effective water | + | :<math> k_o(S_w) =</math> Effective oil permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD |
| − | :<math> k_w =</math> Effective water permeability, mD | + | :<math> k_w(S_w) =</math> Effective water permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> k_o(S_{wc}) =</math> Effective oil permeability at the connate water saturation, mD |
:<math> S_{wc} =</math> Connate water saturation, fraction | :<math> S_{wc} =</math> Connate water saturation, fraction | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Related definitions== | ||
| + | '''Relative permeability curves''' are the relationships between the k<sub>ro</sub> and k<sub>rw</sub> vs S<sub>w</sub>. Corey correlation is a useful approximation for the rel. perm. curves. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Effective permeability''' - oil, water, gas phase permeability when more than one phase is present. Depends on fluids saturations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Absolute permeability''' - permeability of the core sample when saturated with one liquid. Independent of fluid. Dependent on pore throat sizes. | ||
==Example== | ==Example== | ||
| − | Determine the [[ | + | Determine the [[Relative Permeability]] using the following data<ref name=DW/>:<BR> |
| − | Core | + | Core dimensions: A=2 cm2, L=3 cm. PVT: water viscosity = 1 cP, oil viscosity = 3 cP, Bw=1 cc/cc, Bo=1.2 cc/cc. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Absolute permeability=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Core is at 100% water and qw=0.553 cc/sec: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using [[Darcy's law]]: | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> k_{abs} = \frac{0.553*1*1*3}{2*2} = 0.415 D = 415 mD </math> |
| − | + | Same core at 100% oil and qo=0.154 cc/sec: | |
| + | |||
| + | :<math> k_{abs} = \frac{0.154*1.2*3*3}{2*2} = 0.415 D = 415 mD </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Effective permeability=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Same core at 70% water and 30% oil and qw=0.332 cc/sec and qo=0.0184 cc/sec: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> k_w(S_w=0.7)= \frac{0.332*1*1*3}{2*2} = 0.249 D = 249 mD </math> | ||
| + | :<math> k_o(S_w=0.7)= \frac{0.0184*1.2*3*3}{2*2} = 0.049 D = 50 mD </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Same core at 30% connate water and 70% oil and qw=0 cc/sec and qo=0.123 cc/sec: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> k_w(S_{wc}=0.3)= \frac{0*1*1*3}{2*2} = 0 D = 0 mD </math> | ||
| + | :<math> k_o(S_{wc}=0.3)= \frac{0.123*1.2*3*3}{2*2} = 0.332 D = 332 mD </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | SInce Sw=0.3 is connate water saturation, ko=332mD is the effective base permeability. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Relative permeability=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Core at 70% water and 30% oil: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> k_{rw}(S_w=0.7) = \frac{249}{332} = 0.75 </math> | ||
| + | :<math> k_{ro}(S_w=0.7) = \frac{50}{332} = 0.15 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Core at 30% connate water and 70% oil: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> k_{rw}(S_w=0.3) = \frac{0}{332} = 0 </math> | ||
| + | :<math> k_{ro}(S_w=0.3) = \frac{332}{332} = 1 </math> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
*[[Mobility Ratio]] | *[[Mobility Ratio]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[Mature Water Flood Analysis]] | *[[Mature Water Flood Analysis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:35, 2 April 2022
Contents
Brief
Relative Permeability is the ratio of the effective permeability to base oil permeability measured at connate water saturation[1].
where
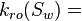 Oil relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction
Oil relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction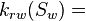 Water relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction
Water relative permeability at the given water saturation Sw, fraction 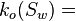 Effective oil permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD
Effective oil permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD 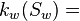 Effective water permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD
Effective water permeability at the given water saturation Sw, mD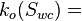 Effective oil permeability at the connate water saturation, mD
Effective oil permeability at the connate water saturation, mD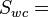 Connate water saturation, fraction
Connate water saturation, fraction
Related definitions
Relative permeability curves are the relationships between the kro and krw vs Sw. Corey correlation is a useful approximation for the rel. perm. curves.
Effective permeability - oil, water, gas phase permeability when more than one phase is present. Depends on fluids saturations.
Absolute permeability - permeability of the core sample when saturated with one liquid. Independent of fluid. Dependent on pore throat sizes.
Example
Determine the Relative Permeability using the following data[1]:
Core dimensions: A=2 cm2, L=3 cm. PVT: water viscosity = 1 cP, oil viscosity = 3 cP, Bw=1 cc/cc, Bo=1.2 cc/cc.
Absolute permeability
Core is at 100% water and qw=0.553 cc/sec:
Using Darcy's law:
Same core at 100% oil and qo=0.154 cc/sec:
Effective permeability
Same core at 70% water and 30% oil and qw=0.332 cc/sec and qo=0.0184 cc/sec:
Same core at 30% connate water and 70% oil and qw=0 cc/sec and qo=0.123 cc/sec:
SInce Sw=0.3 is connate water saturation, ko=332mD is the effective base permeability.
Relative permeability
Core at 70% water and 30% oil:
Core at 30% connate water and 70% oil:
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.