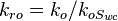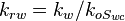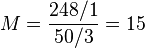Relative Permeability
Brief
Relative Permeability is the ratio of the effective permeability to base oil permeability measured at connate water saturation.
where
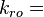 Oil relative permeability, fraction
Oil relative permeability, fraction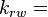 Water relative permeability, fraction
Water relative permeability, fraction 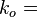 Effective water permeability, mD
Effective water permeability, mD 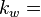 Effective water permeability, mD
Effective water permeability, mD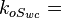 Effective oil permeability at irreducible oil saturation, mD
Effective oil permeability at irreducible oil saturation, mD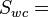 Connate water saturation, fraction
Connate water saturation, fraction
Related definitions
Effective permeability - oil, water, gas phase permeability when more than one phase is present. Depends on fluids saturation.
Absolute permeability - permeability of the core sample when saturated with one liquid. Independent of fluid. Dependent on pore throat sizes.
Example
Determine the Mobility Ratio using the following data[1]:
Core is at 70% water and 30% oil saturation. Water phase permeability is 248 mD, oil phase permeability is 50 mD. Water viscosity is 1 cP, oil viscosity is 3 cP.
In this case the mobility of water is 15 times higher than the mobility of water.
See Also
References
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.