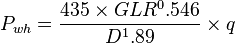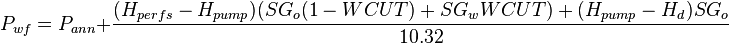Gilbert choke equation
From wiki.pengtools.com
Contents
Brief
The most common used formula for multiphase flow through surface chokes by Gilbert [1].
Echometer is used to measure the fluid level in the wells.
Fluid level is used to calculate and monitor the bottom hole pressure of the wells.
Math and Physics
Flowing well fluids segregation
When the well is flowing with the pump this is how fluids segregate in the well bore:
- Oil, gas and water are produced through the tubing from the reservoir to the surface
- Gas is in the annulus from the surface to the fluid level, Hd
- Oil and gas are between the fluid level Hd, and the pump setting depth, Hd
- Water, oil and gas are between pump, Hd and the top of the perforations, Hperfs
- Water is in the rathole
Equation to calculate the BHP from the fluid level
Note that for the deviated wells TVD depths should be used.
Nomenclature
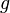 = 9.81, m/s^2
= 9.81, m/s^2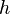 = depth, m
= depth, m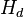 = fluid level, m
= fluid level, m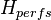 = top of the perforations, m
= top of the perforations, m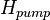 = pump setting depth, m
= pump setting depth, m = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm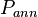 = annulus presssure, atm
= annulus presssure, atm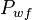 = well flowing bottomhole pressure, atm
= well flowing bottomhole pressure, atm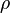 = density, kg/m^3
= density, kg/m^3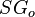 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless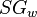 = water specific gravity, dimensionless
= water specific gravity, dimensionless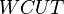 = well water cut, fraction
= well water cut, fraction
References
- ↑ Brown, Kermit (1984). The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods. Volume 4. Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis. Tulsa, Oklahoma: PennWellBookss.