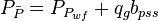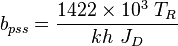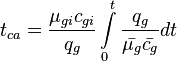Gas Flowing Material Balance
From wiki.pengtools.com
Contents
Brief
Gas Flowing Material Balance is the advanced engineering technique to determine the Reservoirs GIIP and recovery as well as Well's EUR and JD.
Gas Flowing Material Balance is applied on the Well level given readily available well flowing data: production rate and tubing head pressure.
Math & Physics
Combine the gas pseudo state flow equation and the Gas Material Balance equation to get:
Gas Flowing Material Balance equation:
where
Material balance pseudo-time:
Discussion
Workflow
- Convert initial pressure to pseudopressure,
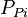
- Convert flowing tubing pressure to flowing bottomhole pressure,
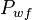
- Convert all flowing pressures to pseudopressures,
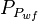
- Calculate material balance pseudo-time,
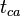
Nomenclature
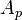 = flow area, ft2
= flow area, ft2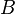 = correlation group, dimensionless
= correlation group, dimensionless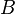 = formation factor, bbl/stb
= formation factor, bbl/stb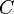 = coefficient for liquid viscosity number, dimensionless
= coefficient for liquid viscosity number, dimensionless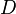 = pipe diameter, ft
= pipe diameter, ft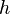 = depth, ft
= depth, ft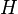 = correlation group, dimensionless
= correlation group, dimensionless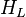 = liquid holdup factor, dimensionless
= liquid holdup factor, dimensionless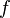 = friction factor, dimensionless
= friction factor, dimensionless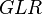 = gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl
= gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl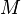 = total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl
= total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl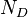 = pipe diameter number, dimensionless
= pipe diameter number, dimensionless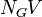 = gas velocity number, dimensionless
= gas velocity number, dimensionless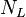 = liquid viscosity number, dimensionless
= liquid viscosity number, dimensionless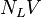 = liquid velocity number, dimensionless
= liquid velocity number, dimensionless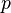 = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia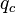 = conversion constant equal to 32.174049, lbmft / lbfsec2
= conversion constant equal to 32.174049, lbmft / lbfsec2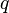 = total liquid production rate, bbl/d
= total liquid production rate, bbl/d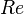 = Reynolds number, dimensionless
= Reynolds number, dimensionless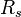 = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb
= solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb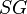 = specific gravity, dimensionless
= specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript
= temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript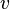 = velocity, ft/sec
= velocity, ft/sec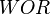 = water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl
= water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl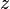 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
Greek symbols
 = absolute roughness, ft
= absolute roughness, ft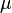 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp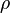 = density, lbm/ft3
= density, lbm/ft3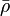 = integrated average density at flowing conditions, lbm/ft3
= integrated average density at flowing conditions, lbm/ft3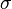 = surface tension of liquid-air interface, dynes/cm (ref. values: 72 - water, 35 - oil)
= surface tension of liquid-air interface, dynes/cm (ref. values: 72 - water, 35 - oil)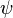 = secondary correlation factor, dimensionless
= secondary correlation factor, dimensionless
Subscripts
- g = gas
- K = °K
- L = liquid
- m = gas/liquid mixture
- o = oil
- R = °R
- SL = superficial liquid
- SG = superficial gas
- w = water
References
- ↑ Mattar, L.; Anderson, D (2005). "Dynamic Material Balance (Oil or Gas-In-Place Without Shut-Ins)" (PDF). CIPC.