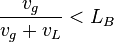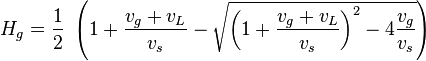P/Z plot
From wiki.pengtools.com
Brief
The P/Z plot is a plot of P/Z versus cumulative gas production, Gp.
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight line to estimate GIIP.
Math & Physics
The P/Z plot method is based on the Gas Material Balance equation.
The bubble flow exist when:
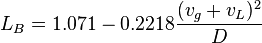 , with the limit
, with the limit 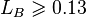 [2]
[2]
The gas holdup:
Discussion
Griffith correlation adds a hook to the originally straight Hagedorn and Brown VLP curve.
Nomenclature
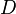 = pipe diameter, ft
= pipe diameter, ft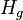 = gas holdup factor, dimensionless
= gas holdup factor, dimensionless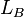 = bubble-slug boundary, dimensionless
= bubble-slug boundary, dimensionless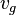 = gas velocity, ft/sec
= gas velocity, ft/sec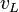 = liquid velocity, ft/sec
= liquid velocity, ft/sec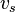 = 0.8, slip velocity (difference between average gas and liquid velocities), ft/sec
= 0.8, slip velocity (difference between average gas and liquid velocities), ft/sec
References
- ↑ Economides, M.J.; Hill, A.D.; Economides, C.E.; Zhu, D. (2013). Petroleum Production Systems (2 ed.). Westford, Massachusetts: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-703158-0.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Orkiszewski, J. (June 1967). "Predicting Two-Phase Pressure Drops in Vertical Pipe"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. SPE. 19 (SPE-1546-PA).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. SPE. 19 (SPE-1546-PA).
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Griffith" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.