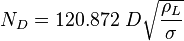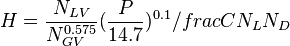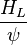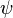Hagedorn and Brown correlation
From wiki.pengtools.com
Contents
Brief
Hagedorn and Brown is an empirical two-phase flow correlation published in 1965.
It doesn't distinguish between the flow regimes.
The heart of the Hagedorn and Brown method is a correlation for the liquid holdup :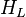 .
.
Math & Physics
Following the law of conservation of energy the basic steady state flow equation is:
where
Colebrook–White equation for the Darcy's friction factor:
Reynolds two phase number:
Discussion
Block Diagram
Workflow
corr p2
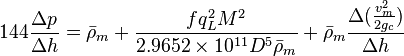
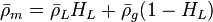
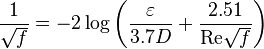
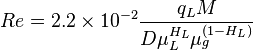
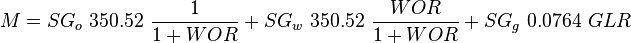
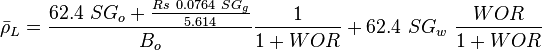
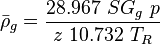
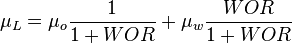
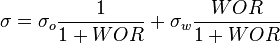
![N_L = 0.15726\ \mu_L \sqrt[4]{\frac{1}{\rho_L \sigma_L^3}}](/images/math/b/2/0/b207fe79b4a4ee53d466e182791ca737.png)
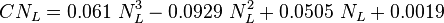
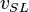
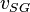
![N_{LV} = 1.938\ v_{SL}\ \sqrt[4]{\frac{\rho_L}{\sigma}}](/images/math/2/f/2/2f2abb2b5e504663beb5ddb87301af09.png)
![N_{GV} = 1.938\ v_{SG}\ \sqrt[4]{\frac{\rho_L}{\sigma}}](/images/math/4/0/c/40cab20a6f3a6a92f320bbff38c696cd.png)