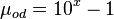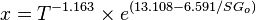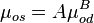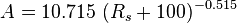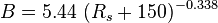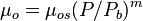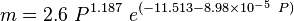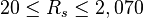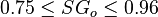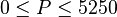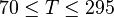Beggs and Robinson Oil Viscosity correlation
From wiki.pengtools.com
Revision as of 12:15, 28 September 2020 by MishaT (talk | contribs) (MishaT moved page Beggs and Robinson correlation to Beggs and Robinson Oil Viscosity correlation: better name)
Contents
Beggs and Robinson Oil Viscosity correlation
Beggs and Robinson is an empirical correlation for the oil viscosity published in 1975 [1].
Math & Physics
Dead oil viscosity:
where:
Saturated oil viscosity (P < Pb):
where:
Undersaturated oil viscosity (P > Pb):
where:
Example. Calculation of the oil viscosity
Example source [3]
Input data
 = 137 F°
= 137 F°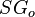 = 0.922 or 22 API
= 0.922 or 22 API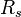 = 90 scf/stb
= 90 scf/stb
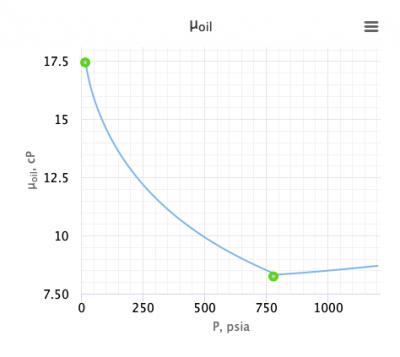
Calculate the saturated oil viscosity?
Solution
x = 1.2658
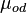 = 17.44 cP
= 17.44 cP
A = 0.719 B = 0.853
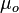 = 8.24 cP
= 8.24 cP
The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software model at www.pengtools.com
Application range
Description of the Data Used[1]:
Number of oil systems = 600
Number of dead oil observations = 460
Number of live oil observations = 2,073
Nomenclature
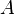 = coefficient
= coefficient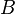 = coefficient
= coefficient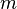 = coefficient
= coefficient = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia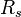 = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb
= solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb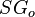 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °F
= temperature, °F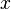 = coefficient
= coefficient
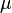 = viscosity, cP
= viscosity, cP
Subscripts
- b - bubble point
- od - dead oil
- os - saturated oil
- o - undersaturated oil
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Beggs, H. D.; Robinson, J. R. (September 1975). "Estimating the Viscosity of Crude Oil Systems"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. 27(09) (SPE-5434-PA).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. 27(09) (SPE-5434-PA).
- ↑
Vasquez, M.; Beggs, H.D. (1980). "Correlations for Fluid Physical Property Prediction."
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-6719-PA).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-6719-PA).
- ↑
Beggs, H. Dale (1987). Oil System Correlations (1987 PEH Chapter 22)
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers.
. Society of Petroleum Engineers.