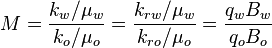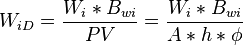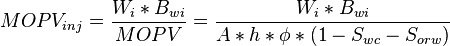Difference between revisions of "Mobility Ratio"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Brief) |
(→Brief) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[Mobility Ratio]] determines the relative rate of one fluid to another (etc. water to oil). | [[Mobility Ratio]] determines the relative rate of one fluid to another (etc. water to oil). | ||
:<math> M \le 1</math> oil is dominant flowing phase, stable flow. | :<math> M \le 1</math> oil is dominant flowing phase, stable flow. | ||
| − | :<math> M > 1</math> water preferentially | + | :<math> M > 1</math> water preferentially flows in the reservoir, unstable flow, fingering. |
| − | |||
===Equation=== | ===Equation=== | ||
Revision as of 14:03, 25 March 2022
Brief
Mobility Ratio determines the relative rate of one fluid to another (etc. water to oil).
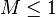 oil is dominant flowing phase, stable flow.
oil is dominant flowing phase, stable flow.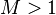 water preferentially flows in the reservoir, unstable flow, fingering.
water preferentially flows in the reservoir, unstable flow, fingering.
Equation
where[1]
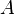 = Area, m2
= Area, m2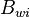 = Injected water formation oil factor, m3/m3
= Injected water formation oil factor, m3/m3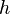 = Net pay, oil saturated thickness, m
= Net pay, oil saturated thickness, m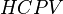 = Hydrocarbon pore volume, m3
= Hydrocarbon pore volume, m3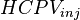 = Injected hydrocarbon pore volumes, fraction
= Injected hydrocarbon pore volumes, fraction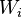 = Cumulative water injection volume, m3
= Cumulative water injection volume, m3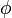 = Porosity, fraction
= Porosity, fraction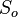 = Oil saturation, fraction
= Oil saturation, fraction
Related definitions
Dimensionless injected pore volume:
Injected movable pore volume:
where
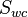 = Connate water saturation, fraction
= Connate water saturation, fraction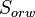 = Residual oil saturation to water, fraction
= Residual oil saturation to water, fraction
See Also
References
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.