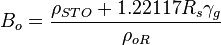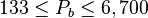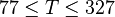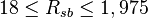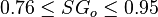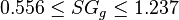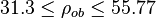Difference between revisions of "McCain Oil Formation Volume Factor equation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→McCain Oil Formation Volume Factor correlation) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math> B_o </math> = oil formation volume factor, rm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> |
| − | + | :<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, sm<sup>3</sup>/sm<sup>3</sup> | |
| − | :<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, | ||
:<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | :<math> SG_g </math> = gas specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
| − | + | :<math> \rho_{oR} </math> = oil density at reservoir conditions, kg/m<sup>3</sup> | |
| − | + | :<math> \rho_{STO} </math> = stock tank oil density, kg/m<sup>3</sup> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> \rho_{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> | ||
| − | |||
===Subscripts=== | ===Subscripts=== | ||
Revision as of 10:38, 28 September 2020
Contents
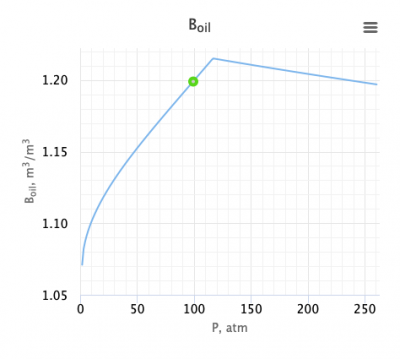
McCain Oil Formation Volume Factor equation
McCain equation is an material balance equation for the oil formation volume factor published in 1990 [1].
Math & Physics
Example. Calculation of the oil density
Example source [2]
Input data
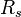 = 53.24 sm3/sm3
= 53.24 sm3/sm3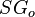 = 0.85 or 35 API
= 0.85 or 35 API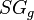 = 0.75
= 0.75 = 90C or 363K
= 90C or 363K = 10 MPa
= 10 MPa
Calculate oil density at p = 10 MPa?
Solution
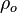 = 749.645 kg/m3
= 749.645 kg/m3
The solution is available in the online PVT calculator software model at www.pengtools.com
Application range
Description of the Data Used[3]:
Number of data sets = 684
Nomenclature
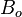 = oil formation volume factor, rm3/sm3
= oil formation volume factor, rm3/sm3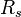 = solution gas-oil ratio, sm3/sm3
= solution gas-oil ratio, sm3/sm3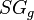 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless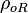 = oil density at reservoir conditions, kg/m3
= oil density at reservoir conditions, kg/m3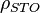 = stock tank oil density, kg/m3
= stock tank oil density, kg/m3
Subscripts
- b - bubble point
- g - gas
- o - oil
References
- ↑ McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351.
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
- ↑ McCain, W.D. Jr.; Hill, N. C. (1995). "Correlations for Liquid Densities and Evolved Gas Specific Gravities for Black Oils During Pressure Depletion"
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-30773-MS).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-30773-MS).