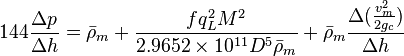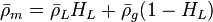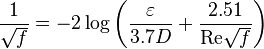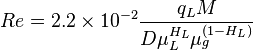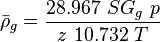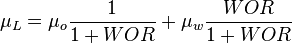Difference between revisions of "Hagedorn and Brown correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Workflow) |
(→Workflow) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
:<math> \bar \rho_g = \frac{28.967\ SG_g\ p}{z\ 10.732\ T} </math> | :<math> \bar \rho_g = \frac{28.967\ SG_g\ p}{z\ 10.732\ T} </math> | ||
| − | :<math> \mu_L = \mu_o \frac{1}{1 + WOR} + \mu_w frac{WOR}{1 + WOR}</math> | + | :<math> \mu_L = \mu_o \frac{1}{1 + WOR} + \mu_w \frac{WOR}{1 + WOR}</math> |
== Block Diagram == | == Block Diagram == | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 20 March 2017
Brief
Hagedorn and Brown is an empirical two-phase flow correlation published in 1965.
It doesn't distinguish between the flow regimes.
The heart of the Hagedorn and Brown method is a correlation for the liquid holdup :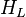 .
.
Math & Physics
Following the law of conservation of energy the basic steady state flow equation is:
where
Colebrook–White equation for the Darcy's friction factor:
Reynolds two phase number: