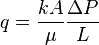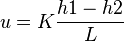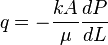Difference between revisions of "Darcy's law"
(→Darcy's law) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Darcy's law History == | == Darcy's law History == | ||
| + | [[File:Darcy's experimental equipment.png|thumb|right|300px| Darcy's experimental equipment]] | ||
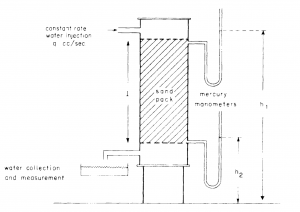
'''Henry Darcy''' worked on the design of a filter large enough to process the Dijon towns daily water requirement <ref name=DakeF/>. | '''Henry Darcy''' worked on the design of a filter large enough to process the Dijon towns daily water requirement <ref name=DakeF/>. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
By flowing water through the sand pack Darcy established that, for any flow rate, the velocity of the flow was directly proportional to the difference in manometric heights<ref name=DakeF/>: | By flowing water through the sand pack Darcy established that, for any flow rate, the velocity of the flow was directly proportional to the difference in manometric heights<ref name=DakeF/>: | ||
| − | + | :<math>u=K\frac{h1-h2}{L}</math> | |
| + | |||
[[File:Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon.png|200px |link=https://books.google.ru/books?id=-FxYAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=twopage&q&f=false]] | [[File:Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon.png|200px |link=https://books.google.ru/books?id=-FxYAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=twopage&q&f=false]] | ||
Revision as of 14:02, 22 July 2019
Contents
Darcy's law
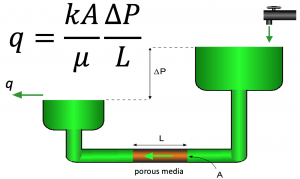
Darcy's law is the fundamental law of fluid motion in porous media published by Henry Darcy in 1856 [1].
Darcy's law has been successfully applied to determine the flow through permeable media since the early days of Petroleum Engineering.
The basic form of Darcy's law is very similar to in form to other physical laws. For example Fourier's law for heat conduction and Ohm's law for flow of electricity [2].
Darcy's law History
Henry Darcy worked on the design of a filter large enough to process the Dijon towns daily water requirement [3].
By flowing water through the sand pack Darcy established that, for any flow rate, the velocity of the flow was directly proportional to the difference in manometric heights[3]:
Darcy's law Equation
Conditions
- Single fluid
- Steady stay flow
- Constant fluid compressibility
- Constant temperature
Inflow Equations Derivation
Derivation of the Linear and Radial Inflow Equations
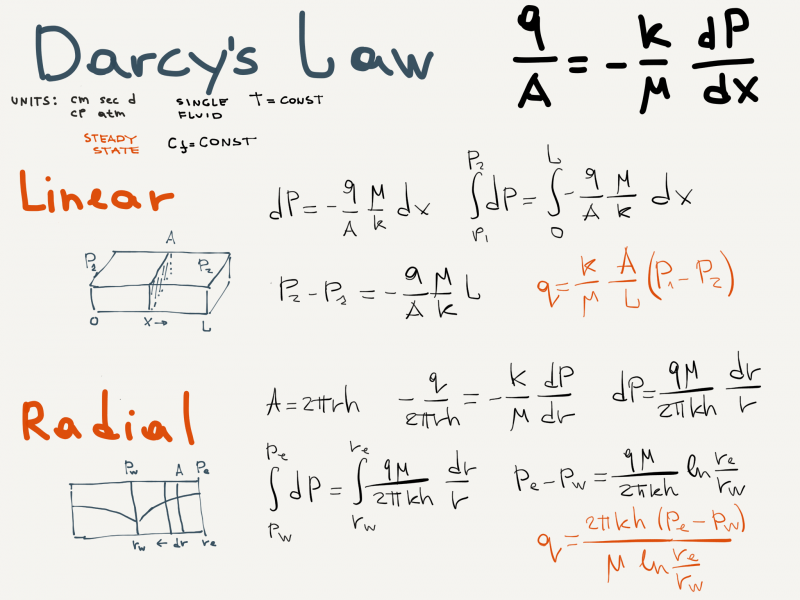
Nomenclature
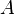 = cross-sectional area, cm2
= cross-sectional area, cm2 = permeability, d
= permeability, d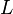 = length, cm
= length, cm = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm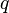 = flow rate, cm3/sec
= flow rate, cm3/sec
Greek symbols
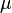 = Darcy's law fluid viscosity, cp
= Darcy's law fluid viscosity, cp
See Also
Darcy's law application in Petroleum Engineering Technology.
References
- ↑ Darcy, Henry (1856). "Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon". Paris: Victor Dalmont.
- ↑
Wolcott, Don (2009). Applied Waterflood Field Development
 . Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
. Houston: Energy Tribune Publishing Inc.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dake, L.P. (1978). Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering. Amsterdam, Hetherlands: Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-444-41830-X.