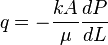Difference between revisions of "Darcy's law"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math and Physics) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
[[File:Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon.png|200px |link=https://books.google.ru/books?id=-FxYAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=twopage&q&f=false]] | [[File:Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon.png|200px |link=https://books.google.ru/books?id=-FxYAAAAYAAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=ru&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=twopage&q&f=false]] | ||
| − | == | + | == Darcy's law Equation == |
:<math> q = -\frac{kA}{\mu} \frac{dP}{dL}</math> | :<math> q = -\frac{kA}{\mu} \frac{dP}{dL}</math> | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 22 March 2019
Contents
Brief
Darcy's law is the fundamental law of fluid motion in porous media published by Henry Darcy in 1856 [1].
Darcy's law Equation
Conditions
- Single fluid
- Steady stay flow
- Constant fluid compressibility
- Constant temperature
Inflow Equations
Derivation of the Linear and Radial Inflow Equations
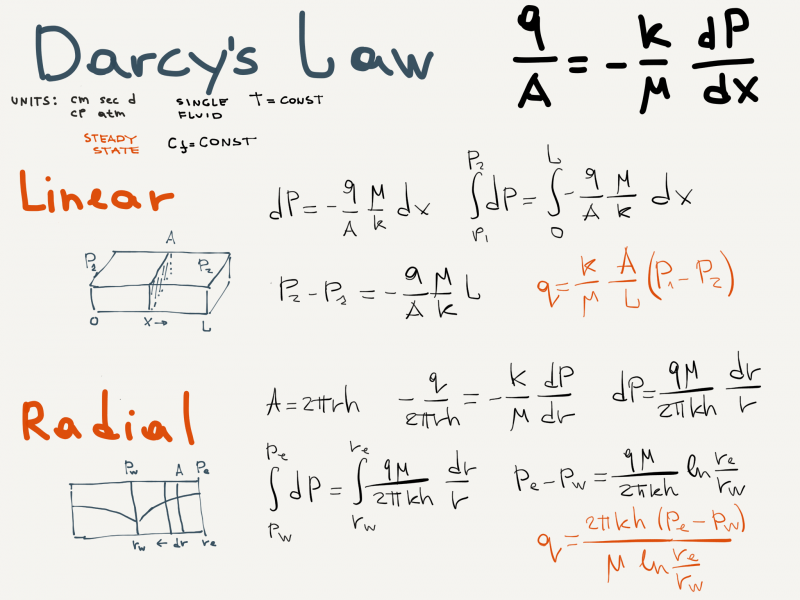
Nomenclature
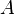 = cross-sectional area, cm2
= cross-sectional area, cm2 = permeability, d
= permeability, d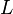 = length, cm
= length, cm = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm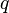 = flow rate, cm3/sec
= flow rate, cm3/sec
Greek symbols
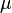 = Darcy's law oil viscosity, cp
= Darcy's law oil viscosity, cp
References
- ↑ Darcy, Henry (1856). "Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon". Paris: Victor Dalmont.