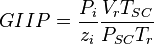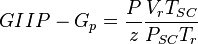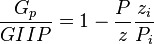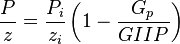Difference between revisions of "P/Z plot"
(→Brief) |
(→Brief) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The [[P/Z plot]] is based on the [[Gas Material Balance]] equation. | The [[P/Z plot]] is based on the [[Gas Material Balance]] equation. | ||
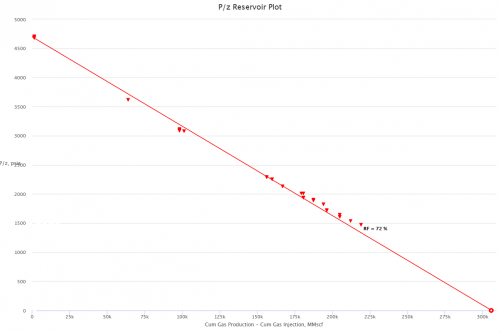
| − | [[File:PoverZ.png|thumb|right| | + | [[File:PoverZ.png|thumb|right|500px|link=https://ep.pengtools.com/reservoir/plots| P/Z plot in the at ep.pengtools.com|right]] |
== Math & Physics == | == Math & Physics == | ||
Revision as of 11:40, 21 November 2017
Brief
The P/Z plot is a plot of P/z versus cumulative gas production, Gp.
The interpretation technique is fitting the data points with the straight line to estimate GIIP.
The P/Z plot is based on the Gas Material Balance equation.
Math & Physics
Applying Real Gas EOS at reservoir conditions:
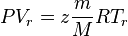 (1)
(1)
Applying Real Gas EOS at standard conditions:
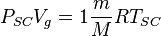 (2)
(2)
Dividing eq. 2 by eq. 1 and rearranging:
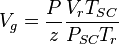 (3)
(3)
Applying eq. 3 for initial conditions and for any point in time:
Applying eq. 3 for any point in time:
Therefore at any time:
Or:
Thus a plot of P/z vs cumulative produced gas is a straight line intersecting X axis at GIIP.
Discussion
P/Z plot is a part of the Reservoir Management workflow of the E&P Portal to estimate Reservoirs GIIP.
Gas Flowing Material Balance is the more advanced tool to determine the Reservoirs GIIP as well as Well's EUR and JD.
Nomenclature
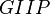 = gas initially in place, scf
= gas initially in place, scf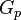 = cumulative gas produced, scf
= cumulative gas produced, scf = reservoir pressure (changing), psia
= reservoir pressure (changing), psia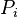 = initial reservoir pressure (constant), psia
= initial reservoir pressure (constant), psia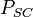 = pressure at standard conditions, psia
= pressure at standard conditions, psia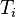 = initial reservoir pressure (constant), °R
= initial reservoir pressure (constant), °R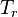 = reservoir pressure (constant), °R
= reservoir pressure (constant), °R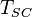 = temperature at standard conditions (constant), °R
= temperature at standard conditions (constant), °R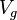 = volume of gas in reservoir converted to standard conditions (changing), scf
= volume of gas in reservoir converted to standard conditions (changing), scf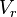 = reservoir volume (constant), ft3
= reservoir volume (constant), ft3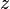 = gas compressibility factor (changing), dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor (changing), dimensionless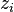 = initial gas compressibility factor (constant), dimensionless
= initial gas compressibility factor (constant), dimensionless