Difference between revisions of "Decline Curve Analysis"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Discussion) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
If one has a need to convert decline factor D<sub>i</sub> to the actual annual decline in %: | If one has a need to convert decline factor D<sub>i</sub> to the actual annual decline in %: | ||
| − | :<math> a = 1 - (1 + b\ D_i) - 1 / b </math> for b > 0 | + | :<math> a = (1 - (1 + b\ D_i)^{- 1 / b}) \times 100 </math> for b > 0 |
| − | :<math> a = 1 - e^{-D_i} </math> for b =1 | + | |
| + | :<math> a = (1 - e^{-D_i}) \times 100</math> for b =1 | ||
=== Nomenclature === | === Nomenclature === | ||
Revision as of 15:56, 26 October 2017
Brief
Decline Curve Analysis DCA is an empirical method for rate decline analysis and rate forecasting published by Arps in 1945 [1].
DCA is applied for Wells and Reservoirs production forecasting.
Math & Physics
| Note | Rate | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperbolic decline, 0 < b < 1 [2] | 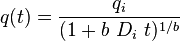 |
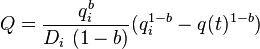 |
| Exponential decline, b = 0 | 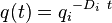 |
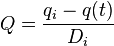 |
| Harmonic decline, b = 1 | 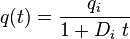 |
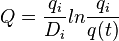 |
Discussion
If one has a need to convert decline factor Di to the actual annual decline in %:
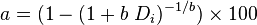 for b > 0
for b > 0
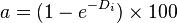 for b =1
for b =1
Nomenclature
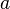 = annual decline, %
= annual decline, %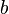 = decline curve parametr, dimensionless
= decline curve parametr, dimensionless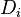 = decline factor per time t, dimensionless
= decline factor per time t, dimensionless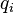 = initial rate, any rate units applies
= initial rate, any rate units applies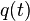 = rate at time t, any rate units applies
= rate at time t, any rate units applies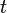 = forecast time, days
= forecast time, days
References
- ↑ Arps, J. J. (1945). "Analysis of Decline Curves"
 . Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 160 (01).
. Transactions of the AIME. Society of Petroleum Engineers. 160 (01).
- ↑ "KAPPA Dynamic Data Analysis (DDA) book"
 .
.
