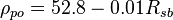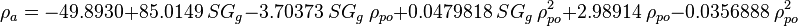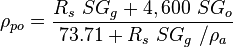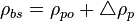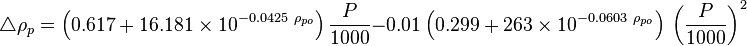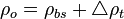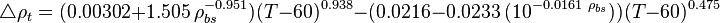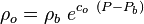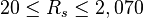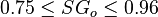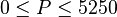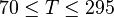Difference between revisions of "McCain Oil density correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→References) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Next pseudoliquid density: | Next pseudoliquid density: | ||
| − | :<math>\rho_{po} = \frac{R_s\ SG_g + 4,600\ SG_o}{73.71+R_s\ SG_g\ / \rho_a}</math> | + | :<math>\rho_{po} = \frac{R_s\ SG_g + 4,600\ SG_o}{73.71+R_s\ SG_g\ / \rho_a}</math><ref name= M1990/> |
Iterate until pseudoliquid densities are equal. | Iterate until pseudoliquid densities are equal. | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 26 July 2017
Contents
Brief
McCain is an empirical correlation for the oil density published in 1995 [1].
Math & Physics
Pseudoliquid density:
Apparent liquid density:
Next pseudoliquid density:
Iterate until pseudoliquid densities are equal.
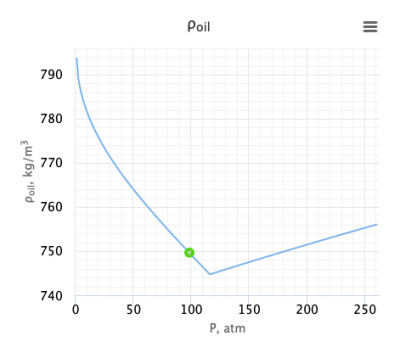
Adjust density to the pressure of interest:
where
Adjust density to the temperature of interest:
where
Adjust density above the bubble point pressure:
Discussion
Application range
Description of the Data Used[1]:
Number of oil systems = 600
Number of dead oil observations = 460
Number of live oil observations = 2,073
Nomenclature
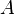 = coefficient
= coefficient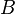 = coefficient
= coefficient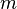 = coefficient
= coefficient = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia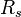 = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb
= solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb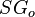 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °F
= temperature, °F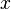 = coefficient
= coefficient
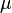 = viscosity, cP
= viscosity, cP
Subscripts
- b - bubble point
- od - dead oil
- os - saturated oil
- o - undersaturated oil
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McCain, W.D. Jr.; Hill, N. C. (1995). "Correlations for Liquid Densities and Evolved Gas Specific Gravities for Black Oils During Pressure Depletion"
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-30773-MS).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-30773-MS).
- ↑ McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351. Invalid
|url-access=paid(help)