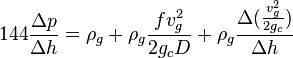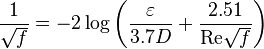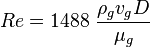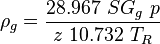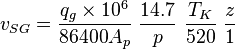Difference between revisions of "Fanning correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Nomenclature) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
:<math> T </math> = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript | ||
:<math> v </math> = velocity, ft/sec | :<math> v </math> = velocity, ft/sec | ||
| − | |||
:<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | :<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | ||
| Line 41: | Line 40: | ||
:<math> \varepsilon </math> = absolute roughness, ft | :<math> \varepsilon </math> = absolute roughness, ft | ||
| − | |||
:<math> \mu </math> = viscosity, cp | :<math> \mu </math> = viscosity, cp | ||
:<math> \rho </math> = density, lb<sub>m</sub>/ft<sup>3</sup> | :<math> \rho </math> = density, lb<sub>m</sub>/ft<sup>3</sup> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Subscripts=== | ===Subscripts=== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 48: | ||
K = °K<BR/> | K = °K<BR/> | ||
L = liquid<BR/> | L = liquid<BR/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
R = °R<BR/> | R = °R<BR/> | ||
| − | |||
SG = superficial gas<BR/> | SG = superficial gas<BR/> | ||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 11:33, 7 April 2017
Contents
Brief
The Fanning correlation is the name used to refer to the calculation of the hydrostatic pressure difference and the friction pressure loss for the dry gas.
Fanning correlation is the default VLP correlation for the dry gas wells in the PQplot.
Math & Physics
Following the law of conservation of energy the basic steady state flow equation is:
Colebrook–White [1] equation for the Darcy's friction factor:
Reynolds number:
Discussion
Why Fanning correlation ?
The Gray correlation was found to be the best of several initially tested ...— Nitesh Kumar l[4]
Nomenclature
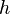 = depth, ft
= depth, ft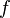 = friction factor, dimensionless
= friction factor, dimensionless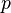 = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia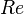 = Reynolds number, dimensionless
= Reynolds number, dimensionless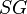 = specific gravity, dimensionless
= specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript
= temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript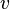 = velocity, ft/sec
= velocity, ft/sec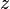 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
Greek symbols
 = absolute roughness, ft
= absolute roughness, ft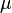 = viscosity, cp
= viscosity, cp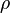 = density, lbm/ft3
= density, lbm/ft3
Subscripts
g = gas
K = °K
L = liquid
R = °R
SG = superficial gas
References
- ↑ Colebrook, C. F. (1938–1939). "Turbulent Flow in Pipes, With Particular Reference to the Transition Region Between the Smooth and Rough Pipe Laws"
 . Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
. Journal of the Institution of Civil Engineers. London, England. 11: 133–156.
- ↑ Moody, L. F. (1944). "Friction factors for pipe flow"
 . Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
. Transactions of the ASME. 66 (8): 671–684.
- ↑ Lyons, W.C. (1996). Standard handbook of petroleum and natural gas engineering. 2. Houston, TX: Gulf Professional Publishing. ISBN 0-88415-643-5.
- ↑ Kumar, N.; Lea, J. F. (January 1, 2005). "Improvements for Flow Correlations for Gas Wells Experiencing Liquid Loading"
 (SPE-92049-MS).
(SPE-92049-MS).
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Gray" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "HB" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.