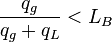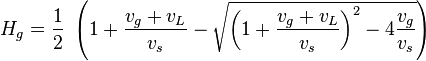Difference between revisions of "Griffith correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→References) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Discussion == | == Discussion == | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math> H_g </math> = gas holdup factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> f </math> = friction factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> GLR </math> = gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> M </math> = total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lb<sub>m</sub>/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> N_D </math> = pipe diameter number number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_GV </math> = gas velocity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_L </math> = liquid viscosity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> N_LV </math> = liquid velocity number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> p </math> = pressure, psia | ||
| + | :<math> q_c </math> = conversion constant equal to 32.174, lb<sub>m</sub>ft / lb<sub>f</sub>sec<sup>2</sup> | ||
| + | :<math> q_L </math> = total liquid production rate, bbl/d | ||
| + | :<math> Re </math> = Reynolds number, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> R_s </math> = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb | ||
| + | :<math> SG </math> = specific gravity, dimensionless | ||
| + | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript | ||
| + | :<math> v </math> = velocity, ft/sec | ||
| + | :<math> WOR </math> = water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl | ||
| + | :<math> z </math> = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 27 March 2017
Brief
The Griffith correlation [1] is an empirical correlation which defines:
- The boundary between the bubble and slug flow[2]
- The void fraction of gas in bubble flow - gas hold up Hg[2]
Math & Physics
The bubble flow exist when:
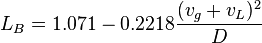 , with the limit
, with the limit 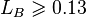 [2]
[2]
The gas holdup:
Discussion
Nomenclature
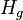 = gas holdup factor, dimensionless
= gas holdup factor, dimensionless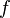 = friction factor, dimensionless
= friction factor, dimensionless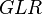 = gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl
= gas-liquid ratio, scf/bbl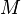 = total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl
= total mass of oil, water and gas associated with 1 bbl of liquid flowing into and out of the flow string, lbm/bbl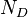 = pipe diameter number number, dimensionless
= pipe diameter number number, dimensionless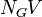 = gas velocity number, dimensionless
= gas velocity number, dimensionless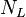 = liquid viscosity number, dimensionless
= liquid viscosity number, dimensionless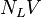 = liquid velocity number, dimensionless
= liquid velocity number, dimensionless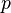 = pressure, psia
= pressure, psia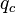 = conversion constant equal to 32.174, lbmft / lbfsec2
= conversion constant equal to 32.174, lbmft / lbfsec2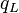 = total liquid production rate, bbl/d
= total liquid production rate, bbl/d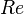 = Reynolds number, dimensionless
= Reynolds number, dimensionless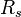 = solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb
= solution gas-oil ratio, scf/stb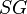 = specific gravity, dimensionless
= specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript
= temperature, °R or °K, follow the subscript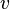 = velocity, ft/sec
= velocity, ft/sec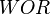 = water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl
= water-oil ratio, bbl/bbl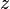 = gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
= gas compressibility factor, dimensionless
References
- ↑ Griffith, P.; Wallis, G. B. (August 1961). "Two-Phase Slug Flow"
 . Journal of Heat Transfer. ASME. 83: 307–320.
. Journal of Heat Transfer. ASME. 83: 307–320.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Orkiszewski, J. (June 1967). "Predicting Two-Phase Pressure Drops in Vertical Pipe"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. SPE. 19 (SPE-1546-PA).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. SPE. 19 (SPE-1546-PA).