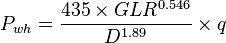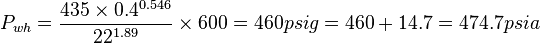Difference between revisions of "Gilbert choke equation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math and Physics) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
:<math>GLR</math> = gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl | :<math>GLR</math> = gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl | ||
:<math>P_{wh}</math> = well head pressure, psig | :<math>P_{wh}</math> = well head pressure, psig | ||
| − | :<math>q</math> = flow rate, bbl/d | + | :<math>q</math> = liquid flow rate, bbl/d |
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 8 November 2024
Contents
Brief
The most common formula used for multiphase flow through surface chokes by Gilbert [1].
Gilbert developed his empirical equation from field data in California[2].
Math and Physics
Note that the equation is independent of the downstream pressure and assumes that the downstream pressure is less than 70% of the upstream pressure, i.e. the flow is "critical" i.e. fluid reach sonic velocity in the throat of the choke.
Example
Given data
Oil rate = 600 bbl/d, GLR=400 scf/bbl, D=22/64 in, Line pressure = 180 psia
Calculate the well head pressure?
Solution
Validity check 180/474.7=0.38 < 0.7 OK
Nomenclature
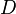 = choke beam diametr, 64th of an inch
= choke beam diametr, 64th of an inch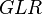 = gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl
= gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl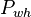 = well head pressure, psig
= well head pressure, psig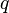 = liquid flow rate, bbl/d
= liquid flow rate, bbl/d
References