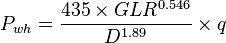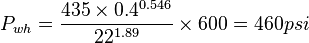Difference between revisions of "Gilbert choke equation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Example) |
(→Example) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
===Solution=== | ===Solution=== | ||
| − | :<math>P_{wh}=\frac{435 \times 0.4^{0.546}}{22^{1.89}} \times 600 = 460 | + | :<math>P_{wh}=\frac{435 \times 0.4^{0.546}}{22^{1.89}} \times 600 = 460 psi</math> |
Check validity 180/460=0.4 - OK | Check validity 180/460=0.4 - OK | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 8 November 2024
Contents
Brief
The most common formula used for multiphase flow through surface chokes by Gilbert [1][2].
Gilbert developed his equation from field data in California.
Math and Physics
Note that the equation is independent of the downstream pressure and assumes that the downstream pressure is less than 70% of the upstream pressure.
Example
Given data
Oil rate = 600 bbl/d, GLR=400 scf/bbl, D=22/64 in, Line pressure = 180 psi
Calculate well head pressure?
Solution
Check validity 180/460=0.4 - OK
Nomenclature
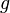 = 9.81, m/s^2
= 9.81, m/s^2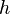 = depth, m
= depth, m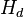 = fluid level, m
= fluid level, m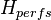 = top of the perforations, m
= top of the perforations, m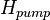 = pump setting depth, m
= pump setting depth, m = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm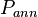 = annulus presssure, atm
= annulus presssure, atm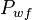 = well flowing bottomhole pressure, atm
= well flowing bottomhole pressure, atm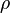 = density, kg/m^3
= density, kg/m^3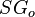 = oil specific gravity, dimensionless
= oil specific gravity, dimensionless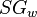 = water specific gravity, dimensionless
= water specific gravity, dimensionless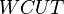 = well water cut, fraction
= well water cut, fraction
References