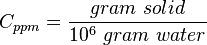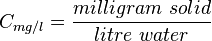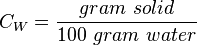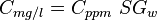Difference between revisions of "Water bubble point pressure"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(Created page with "__TOC__ ==Water bubble point pressure== The concentration of solids in formation water (brines) are reported in several different ways <ref name= M1990/>. ==Math and Physics...") |
(→Water bubble point pressure) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Water bubble point pressure== | ==Water bubble point pressure== | ||
| − | The | + | The bubble point of a gas-saturated formation water (brine) is equal to the bubble point pressure of coexisting oil <ref name= M1990/>. |
| + | |||
| + | The two are equal because of thermodynamic equilibrium between the brine and the oil. | ||
==Math and Physics== | ==Math and Physics== | ||
Revision as of 05:35, 1 October 2020
Contents
Water bubble point pressure
The bubble point of a gas-saturated formation water (brine) is equal to the bubble point pressure of coexisting oil [1].
The two are equal because of thermodynamic equilibrium between the brine and the oil.
Math and Physics
Conversions
Often, parts per million and milligrams per liter are used interchangeably. This is correct only if the density of the brine at standard conditions can be assumed to be 1 g/cc ( 1000 kg/m3, SG_w=1, 62.428 lbm/ft3) [1].
Nomenclature
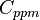 = water salinity or solids concentration, ppm
= water salinity or solids concentration, ppm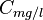 = water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l
= water salinity or solids concentration, mg/l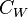 = water salinity or weight percent solids, %
= water salinity or weight percent solids, %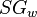 = water specific gravity, dimensionless
= water specific gravity, dimensionless
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 McCain, W.D. Jr. (1990). Properties of Petroleum Fluids (2 ed.). Oklahoma: PennWell Corp. ISBN 978-0878143351.