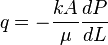Difference between revisions of "Darcy's law"
From wiki.pengtools.com
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| − | :<math> q </math> = | + | :<math> q </math> = flow area, cm<sup>2</sup> |
| − | + | :<math> k</math> = permeability, d | |
| − | :<math> k</math> = | + | :<math> L </math> = length, cm |
| − | :<math> L </math> = | + | :<math> P </math> = pressure, atm |
| − | :<math> P </math> = | + | :<math> q </math> = flow rate, cm<sup>3</sup>/sec |
| − | :<math> q </math> = | ||
===Greek symbols=== | ===Greek symbols=== | ||
Revision as of 06:41, 23 April 2018
Brief
Darcy's law is the fundamental law of fluid motion in porous media published by Henry Darcy in 1856 [1].
Math and Physics
Conditions
- Single fluid
- Steady stay flow
- Constant fluid compressibility
- Constant temperature
Nomenclature
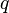 = flow area, cm2
= flow area, cm2 = permeability, d
= permeability, d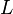 = length, cm
= length, cm = pressure, atm
= pressure, atm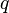 = flow rate, cm3/sec
= flow rate, cm3/sec
Greek symbols
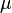 = Darcy's law oil viscosity, cp
= Darcy's law oil viscosity, cp
References
- ↑ Darcy, Henry (1856). "Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon". Paris: Victor Dalmont.