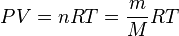Difference between revisions of "Ideal Gas"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Nomenclature) |
(→Nomenclature) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
:<math> m </math> = mass, lb<sub>m</sub> | :<math> m </math> = mass, lb<sub>m</sub> | ||
:<math> M </math> = molecular weight, lb<sub>m</sub>/lb<sub>mol</sub> | :<math> M </math> = molecular weight, lb<sub>m</sub>/lb<sub>mol</sub> | ||
| − | :<math> n </math> = number of moles | + | :<math> n </math> = number of moles, lb<sub>mol</sub> |
:<math> P </math> = Pressure, psia | :<math> P </math> = Pressure, psia | ||
:<math> R </math> = universal gas constant, 10.7316 psia ft<sup>3</sup>/ lb<sub>mol</sub>/ °R | :<math> R </math> = universal gas constant, 10.7316 psia ft<sup>3</sup>/ lb<sub>mol</sub>/ °R | ||
:<math> T </math> = temperature, °R | :<math> T </math> = temperature, °R | ||
:<math> V </math> = volume, ft<sup>3</sup> | :<math> V </math> = volume, ft<sup>3</sup> | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 20 November 2017
Brief
Ideal Gas is a concept where:
- gas is composed with molecules of negligible volume;
- interaction between the molecules is negligible.
Equation Of State
It all started with Boyle-Charles Law published in 1662 .
The Ideal Gas EOS:
Nomenclature
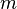 = mass, lbm
= mass, lbm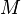 = molecular weight, lbm/lbmol
= molecular weight, lbm/lbmol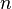 = number of moles, lbmol
= number of moles, lbmol = Pressure, psia
= Pressure, psia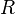 = universal gas constant, 10.7316 psia ft3/ lbmol/ °R
= universal gas constant, 10.7316 psia ft3/ lbmol/ °R = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R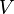 = volume, ft3
= volume, ft3