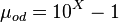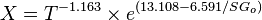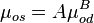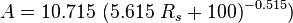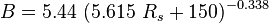Difference between revisions of "Beggs and Robinson Oil Viscosity correlation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math & Physics) |
(→Math & Physics) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
where: | where: | ||
| − | + | :<math> A = 10.715\ (5.615\ R_s + 100)^{-0.515}) </math> | |
| − | + | :<math> B = 5.44\ ( 5.615\ R_s + 150)^{-0.338} </math> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Discussion === | === Discussion === | ||
Revision as of 09:42, 25 July 2017
Contents
Brief
Beggs - Robinson is an empirical correlation for the oil viscosity published in 1975 [1].
Math & Physics
Dead oil viscosity:
where:
Saturated oil viscosity:
where:
Discussion
Workflow
Application range
Nomenclature
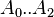 = coefficients
= coefficients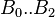 = coefficients
= coefficients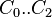 = coefficients
= coefficients = pressure, MPA
= pressure, MPA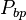 = bubble point pressure, MPA
= bubble point pressure, MPA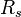 = oil gas ration, m3/m3
= oil gas ration, m3/m3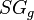 = gas specific gravity, dimensionless
= gas specific gravity, dimensionless = temperature, °R
= temperature, °R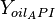 = oil API gravity, dimensionless
= oil API gravity, dimensionless
References
- ↑ Beggs, H. D.; Robinson, J. R. (September 1975). "Estimating the Viscosity of Crude Oil Systems"
 . Journal of Petroleum Technology. 27(09) (SPE-5434-PA).
. Journal of Petroleum Technology. 27(09) (SPE-5434-PA).
- ↑
Vazquez, M.; Beggs, H.D. (1980). "Correlations for Fluid Physical Property Prediction."
 . Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-6719-PA).
. Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE-6719-PA).