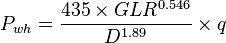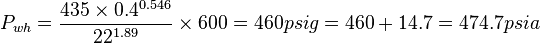Difference between revisions of "Gilbert choke equation"
From wiki.pengtools.com
(→Math and Physics) |
(→Brief) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | <div style='text-align: right;'>By Mikhail Tuzovskiy on {{REVISIONTIMESTAMP}}</div> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
==Brief== | ==Brief== | ||
| − | The most common used | + | The most common formula used for multiphase flow through surface chokes developed by '''Gilbert''' in 1954<ref name=Gilbert/>. |
| − | + | Gilbert developed his empirical equation from field data in California<ref name=KermitBrown1984/>. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Math and Physics== | ==Math and Physics== | ||
:<math>P_{wh}=\frac{435 \times GLR^{0.546}}{D^{1.89}} \times q</math> | :<math>P_{wh}=\frac{435 \times GLR^{0.546}}{D^{1.89}} \times q</math> | ||
| − | + | Note that the equation is independent of the downstream pressure and assumes that the downstream pressure is less than 70% of the upstream pressure, i.e. the flow is "critical" i.e. fluid reach sonic velocity in the throat of the choke<ref name=Economides/>. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Example== | |
| − | + | ===Given data=== | |
| − | + | Oil rate = 600 bbl/d, GLR=400 scf/bbl, D=22/64 in, Line pressure = 180 psia | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Calculate the well head pressure? | |
| − | === | + | ===Solution=== |
| − | :<math>P_{ | + | :<math>P_{wh}=\frac{435 \times 0.4^{0.546}}{22^{1.89}} \times 600 = 460 psig = 460 +14.7 = 474.7 psia</math> |
| − | + | Validity check 180/474.7=0.38 < 0.7 OK | |
==Nomenclature== | ==Nomenclature== | ||
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>D</math> = choke beam diametr, 64th of an inch |
| − | + | :<math>GLR</math> = gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl | |
| − | + | :<math>P_{wh}</math> = well head pressure, psig | |
| − | + | :<math>q</math> = liquid flow rate, bbl/d | |
| − | :<math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math>P_{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name= Gilbert>{{cite book | ||
| + | |last1= Gilbert |first1= W.E. | ||
| + | |title=Flowing and Gas-Lift Well Performance | ||
| + | |journal=Drilling and Production Practice API | ||
| + | |date=1954 | ||
| + | |page=143 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
<ref name= KermitBrown1984 >{{cite book | <ref name= KermitBrown1984 >{{cite book | ||
|last1= Brown |first1= Kermit | |last1= Brown |first1= Kermit | ||
| Line 46: | Line 44: | ||
|place=Tulsa, Oklahoma | |place=Tulsa, Oklahoma | ||
}}</ref> | }}</ref> | ||
| − | + | <ref name=Economides>{{cite book | |
| + | |last1= Economides |first1=M.J. | ||
| + | |last2= Hill |first2=A.D. | ||
| + | |last3= Economides |first3=C.E. | ||
| + | |last4= Zhu |first4=D. | ||
| + | |title=Petroleum Production Systems | ||
| + | |edition=2 | ||
| + | |date=2013 | ||
| + | |publisher=Prentice Hall | ||
| + | |place=Westford, Massachusetts | ||
| + | |isbn=978-0-13-703158-0 | ||
| + | }}</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 8 November 2024
By Mikhail Tuzovskiy on 20241108191031
Contents
Brief
The most common formula used for multiphase flow through surface chokes developed by Gilbert in 1954[1].
Gilbert developed his empirical equation from field data in California[2].
Math and Physics
Note that the equation is independent of the downstream pressure and assumes that the downstream pressure is less than 70% of the upstream pressure, i.e. the flow is "critical" i.e. fluid reach sonic velocity in the throat of the choke[3].
Example
Given data
Oil rate = 600 bbl/d, GLR=400 scf/bbl, D=22/64 in, Line pressure = 180 psia
Calculate the well head pressure?
Solution
Validity check 180/474.7=0.38 < 0.7 OK
Nomenclature
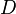 = choke beam diametr, 64th of an inch
= choke beam diametr, 64th of an inch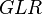 = gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl
= gas liquid ratio, Mscf/bbl or 10^3 scf/bbl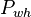 = well head pressure, psig
= well head pressure, psig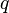 = liquid flow rate, bbl/d
= liquid flow rate, bbl/d
References
- ↑ Gilbert, W.E. (1954). Flowing and Gas-Lift Well Performance. Drilling and Production Practice API. p. 143.
- ↑ Brown, Kermit (1984). The Technology of Artificial Lift Methods. Volume 4. Production Optimization of Oil and Gas Wells by Nodal System Analysis. Tulsa, Oklahoma: PennWellBookss.
- ↑ Economides, M.J.; Hill, A.D.; Economides, C.E.; Zhu, D. (2013). Petroleum Production Systems (2 ed.). Westford, Massachusetts: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-703158-0.